VCmaster US Catalog 01concrete01-51.en - Id
VCmaster US Catalog 01concrete01-51.en - Id
Diunggah oleh
Tony WangJudul Asli
Hak Cipta
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniVCmaster US Catalog 01concrete01-51.en - Id
VCmaster US Catalog 01concrete01-51.en - Id
Diunggah oleh
Tony WangContoh untuk ACI, AISC dan ASCE KAMI
Perhitungan Template interaktif dengan kode AS Halaman 1
Contoh untuk ACI, AISC dan ASCE
KAMI
Perhitungan Template interaktif dengan kode AS
ACI 318-11
Tidak ada yang mengalahkan TEMPLATE BESAR
Kata pengantar
kadar
bantu desain interaktif sesuai dengan kode US ACI 318-11, AISC 14 th Edisi dan ASCE-7-10
Pedoman penggunaan
Setelah menginstal percobaan atau demo versi gratis template interaktif akan tersedia secara gratis. Satu-satunya persyaratan adalah
pendaftaran di www.VCmaster.com.
Contoh-contoh yang telah dibuat menggunakan VCmaster. Semua dijelaskan dan alat bantu desain diilustrasikan dapat digunakan sebagai dasar
untuk membuat template sendiri. Untuk melakukan ini versi lengkap dari VCmaster diperlukan.
Semua template terkait dengan berbagai database oleh TAB () - atau SEL () fungsi. Untuk tujuan instruksional link ini ditampilkan dalam
dokumen ini, tetapi juga dapat disembunyikan saat mencetak.
Apa VCmaster?
VCmaster adalah aplikasi perangkat lunak untuk dokumentasi teknis khusus dirancang untuk insinyur. Konsep perangkat lunak yang unik
mengintegrasikan semua desain dan CAD struktural software. antarmuka Universal menjamin transfer data yang mudah, sehingga output
dari semua program dapat dialihkan.
Disamping fungsinya untuk dokumentasi, VCmaster menawarkan konsep intuitif memungkinkan para insinyur untuk melakukan perhitungan.
Masukan dari rumus matematika dapat dilaksanakan dalam notasi alami langsung dalam dokumen itu sendiri. Perangkat lunak ini secara
signifikan mendukung penggunaan kembali perhitungan struktural dan dokumen. VCmaster menyederhanakan modifikasi dan penyesuaian dan
mengotomatisasi tugas-tugas standar. Kolaborasi dengan pekerjaan-kelompok atau dengan kantor-kantor lain dan klien tidak rumit juga.
Akibatnya, waktu pemrosesan dan biaya dapat sangat dikurangi.
Persyaratan sistem
VCmaster 2017 atau yang lebih baru
Pengembangan dan Hak Cipta
VCmaster telah dikembangkan di Jerman VCmaster adalah
merek dagang terdaftar Semua template yang dibuat di
Amerika Serikat © Veit Christoph GmbH 1995-2018
www.VCmaster.com
Interaktif Desain Aids untuk Engineers Struktural
Contoh untuk ACI, AISC dan ASCE KAMI
Perhitungan Template interaktif dengan kode AS Halaman 2
Isi
Bab 1: Desain Beton 4
Corbel Desain 4
Pracetak gerbang Beam untuk Gabungan Shear dan Torsion 7
Beam Ledge Desain 11
Rectangular Bagian dengan Ketegangan Penguatan 14
Rectangular Bagian dengan Kompresi Penguatan 16
Tulangan Geser untuk Bagian Tunduk Q & N 19
Tulangan Geser untuk Bagian Tunduk Q & T 22
Defleksi Bagian Composite ditopang 24
Desain lentur Bagian bergelang 28
Cracking Momen Kekuatan untuk Bagian Pratekan 31
Kekuatan lentur Pratekan Anggota 32
Ketegangan Controlled Batas untuk Pratekan Lentur Anggota 34
Kerugian Prestress 36
Meninju Tulangan Geser pada Slab 39
One Way balok silang 41
Dua Way Slab Dilihat Metode Desain Direct 47
Pengembangan Panjang Bar di Tension 50
Kelompok Berambut Studs di Ketegangan dekat Ujung 52
Geser Kekuatan Slab pada Dukungan Kolom 54
Sederhana Span Jauh Beam oleh Strut-and-Tie Model 56
Terus menerus Jauh Beam oleh Strut-and-Tie Model 60
Transfer Horizontal Angkatan di Base of Kolom 65
Bantalan Dinding dengan Metode Empiris 67
Geser Desain Dinding 70
Gesekan geser 73
Tunggal Adhesive jangkar di Ketegangan 75
Tunggal Berambut Jangkar Bolt di Ketegangan 77
Tunggal Berambut Jangkar Bolt di Shear dekat Ujung 79
Defleksi Beam Sederhana 81
Tulangan Geser untuk Bagian Tunduk Q & M 84
Penguatan geser pada Pembukaan 87
Horisontal Shear untuk Komposit Slab dan Precast Beam 90
Interaktif Desain Aids untuk Engineers Struktural
Contoh untuk ACI, AISC dan ASCE KAMI
Perhitungan Template interaktif dengan kode AS Halaman: 3
Bab 2: Yayasan Desain 92
Penguatan Yayasan Dangkal 92
Kedalaman Yayasan Dangkal 95
Mendalam untuk Pile Cap 98
Slab di kelas 101
Bab 3: Baja Desain 102
W-Bentuk dalam Kuat Axis Bending, Bersiap di Beberapa Poin 102
W-Shape di Kuat Axis Bending, Terus Bersiap 106
W-Shape di Kecil Axis Bending 109
W-Shape Dikenakan Angkatan Ketegangan dan Bending Moments 112
W-Bentuk dalam Axial Kompresi 117
WT-Bentuk dalam Axial Kompresi 120
Built-Up W-Shapes dengan Slender Elements 124
W-Bentuk Dikenakan Kompresi dan Lentur 128
W-Shape Dikenakan P dan M termasuk Effect Orde Kedua 134
HSS-Shape di Kuat Axis Bending 140
W-Shape Dikenakan Angkatan Ketegangan di Connection baut: 143
WT-Shape Dikenakan Angkatan Ketegangan di Koneksi Dilas 146
Interior Panel dari Built-Up Girder dengan Transverse pengaku 149
End Panel dari Built-Up Girder dengan Transverse pengaku 151
Komposit Beam Dikenakan Lentur 153
Bab 4: Desain Connection 159
Plat dasar Dikenakan Memuat konsentris 159
Plat dasar Dikenakan Eksentrisitas Kecil 161
Plat dasar Dikenakan Eksentrisitas Besar 164
Lug geser 167
Fillet Weld Dikenakan Longitudinal Shear Angkatan 169
Baut di Bantalan Jenis Koneksi Dikenakan T & V 171
Menyelinap Kritis Koneksi dengan Short-Slotted Lubang 173
Bab 5: Banyak Desain 175
beban angin untuk Walls berdiri bebas Solid & Tanda 175
Banyak salju untuk Roof datar 178
Banyak salju untuk miring Atap 179
Seismik Basis Shear 180
Interaktif Desain Aids untuk Engineers Struktural
Bab 1: Desain Beton ACI 318
Corbel Desain Halaman: 4
Bab 1: Desain Beton
ACI 318
Desain Corbel sesuai ACI 318-11 Bab 11
Corbel Desain
vu
asc av
NUC
23 d
h d co
ah
Sistem
Corbel Lebar, b = 14,0 di
Corbel Tinggi, h = 12,0 di
Beton Cover, co = 1.0 di
Corbel Kedalaman, d = co- h = 12.0 1.0
- = 11.0 di
Jarak dari Kolom Tatap beban vertikal, sebuah v = 3.0 di
Beban
Beban Ultimate vertikal, V u = 88,8 kips
Ultimate Horizontal beban, NUC = 32,0 kips
Properti materi
Beton Kekuatan, f' c = 5000 psi
Yield Kekuatan Tulangan, f y = 60000 psi
Kekuatan Geser Faktor Reduksi (Menurut Cl.9.3.2 dari ACI318), • = 0,75
Modifikasi Factor untuk Beton Ringan, •• • 1.00
Gesekan Factor (Menurut Cl.11.6.4.3 dari ACI318), • = 1,4 * • = 1,40
Interaktif Desain Aids untuk Engineers Struktural
Bab 1: Desain Beton ACI 318
Corbel Desain Halaman: 5
Periksa Vertikal Kapasitas Angkut
V = n1 0,2 * f' c * b * d / 1000 = 154,0 Kips
V = n2 (480 + 0,08 * f' c) * b * d / 1000 = 135,5 Kips
V = n3 1600 * b * d / 1000 = 246.4 Kips
Nominal Kapasitas Vertikal (Menurut Cl.11.8.3.2.1 dari ACI318),
• Vn= • • MIN (V n1; V n2; V n3) = 101,6 Kips
Vertikal Kapasitas Angkut = IF (V u> • V n;" Tidak Lulus ";" Lulus ") = Lulus
Tentukan Shear Gesekan Tulangan (A vf)
Diperlukan Luas Tulangan untuk Gesekan Shear (Menurut Cl.11.6.4.1 dari ACI318), A vf =
V u 1000 • / ו × × f y •• = 1,41 in²
Tentukan Ketegangan Penguatan Langsung (A n)
Minimum Horizontal Angkatan pada Corbel, Nuc_min = 0,2 V×u = 17,8 Kips
Horizontal Angkatan pada Corbel, Nuc_act = MAX (NUC; Nuc_min) = 32,0 kips
Diperlukan Luas Tulangan untuk Tension Langsung (Menurut Cl.11.8.3.1 dari ACI318), A n =
* •
Nuc_act 1000 / •• • * fy • = 0,71 in²
Tentukan Tulangan Lentur (A f)
Mu= V u * Sebuah v + Nuc_act * (hd) = 298,4 kip * di
Diperlukan Luas Tulangan untuk Lentur (Menurut Cl.11.8.3.3 dari ACI318), A f =
M u 1000 • / ו × × f 0,9
y d× • = 0,67 in²
Tentukan Penguatan Ketegangan Primer (A sc)
Diperlukan Luas Tulangan untuk Tension Primer (Menurut Cl.11.8.3.5 dari ACI318),
SEBUAH sc = MAX ((2/3 * A vf) + SEBUAH n; SEBUAH f + SEBUAH n) = 1,65 di 2
Lokasi minimal Tulangan untuk Tension Primer (Menurut Cl.11.8.5 dari ACI318), A sc_min =
0,04 * / F' c f*y bd
* = 0,51 in²
SEBUAH sc_Req = MAX (A sc; SEBUAH sc_min) = 1,65 in²
Asalkan Penguatan, Bar = SEL ( "ACI / Bar"; Bar;) = no.9
Tersedia Area Bar Penguatan, A sb = TAB ( "ACI / Bar"; Asb; Bar = Bar) = 1.00 di 2
Jumlah bar Asalkan, n = 2
Tersedia Area Penguatan, A sc_Prov = n * A sb = 2.00 di 2
Periksa Validitas = JIKA SEBUAH sc_Prov • SEBUAH sc_Req; " Hari "; "valid") = Sah
Interaktif Desain Aids untuk Engineers Struktural
Bab 1: Desain Beton ACI 318
Corbel Desain Halaman: 6
Tentukan Horizontal Penguatan (A h)
Diperlukan Luas Tulangan untuk Horizontal geser (Menurut Cl.11.8.4 dari ACI318), A h_Req =
0,5 * (A sc_Prov- SEBUAH n) = 0.65 in²
Asalkan Penguatan, Bar = SEL ( "ACI / Bar"; Bar;) = Nomor 3
Tersedia Area Bar Penguatan, A sb = TAB ( "ACI / Bar"; Asb; Bar = Bar) = 0,11 di 2
Jumlah bar Asalkan, n = 6
Tersedia Area Penguatan, A h_Prov = n * A sb = 0,66 di 2
Periksa Validitas = JIKA SEBUAH h_Prov • SEBUAH h_Req; " Hari "; "valid") = Sah
Mendistribusikan dalam dua-pertiga dari Corbel Efektif Kedalaman berdekatan dengan A sc
desain Ringkasan
Daerah Tulangan untuk Ketegangan Primer A sc = SEBUAH sc_Prov = 2.00 in²
Daerah Tulangan untuk Horizontal Shear, A h = SEBUAH h_Prov = 0,66 in²
Mendistribusikan dalam dua-pertiga dari Corbel Efektif Kedalaman berdekatan dengan A sc
Interaktif Desain Aids untuk Engineers Struktural
Bab 1: Desain Beton ACI 318
Pracetak gerbang Beam untuk Gabungan Shear dan Torsion Halaman: 7
Design Precast Spandrel Beam for Combined Shear and Torsion as per ACI 318-11 Chapter 11
Precast Spandrel Beam for Combined Shear and Torsion
A' v
AlA
h sc
hL
b bL
System
Width of Beam, b= 16.0 in
Height of Beam, h= 48.0 in
Width of Beam Ledge, b L= 8.0 in
Height of Beam Ledge, h L= 16.0 in
Concrete Cover, co= 2.50 in
Concrete Cover to Center of Stirrup, co'= 1.50 in
Effective Depth of Beam, d= co- h = 45.50 in
Load
Ultimate Bending Moment, M u= 1316.0 kip*ft
Ultimate Torsional Moment, T u= 108.6 kip*ft
Ultimate Shear Force, V u= 127.2 kips
Material Properties
Concrete Strength, f' c= 5000 psi
Yield Strength of Reinforcement, f y= 60000 psi
Yield Strength of Stirrups Reinforcement, f yt= 60000 psi
Shear Strength Reduction Factor (According to Cl.9.3.2 of ACI318), • s= 0.75
Tension Strength Reduction Factor (According to Cl.9.3.2 of ACI318), • t= 0.90
Modification Factor for Lightweight Concrete, •• • 1.00
Friction Factor (According to Cl.11.6.4.3 of ACI318), •= 1.4* • = 1.40
Interactive Design Aids for Structural Engineers
Chapter 1: Concrete Design ACI 318
Precast Spandrel Beam for Combined Shear and Torsion Page: 8
Determine Concrete Cracking Torque
Area Enclosed by Outside Perimeter of Spandrel Beam Including the Ledge,
A cp= b*h+bL*hL = 896 in 2
Outside Perimeter of Spandrel Beam Including the Ledge, P cp=
2 * (b + b L + h) = 144 in
2
A cp
4* • f' c * / 12000
Concrete Cracking Torque, T cr= *
• P cp
= 131.4 kip*ft
Torsional Moment should be: IF(T u< • s* T cr/ 4;"Neglected";"Checked") = Checked
Calculation of Torsion Reinforcement
Area Enclosed by Centerline of The Outermost Closed Transverse Torsional Reinforcement (According to
Cl.11.5.3.6 of ACI318),
A oh= (h-2*co')*(b-2*co')+(b L)*( h L- 2*co') = 689.0 in 2
A o= 0.85*A oh = 585.6 in 2
Angle of Compression Diagonal Struts (According to 11.5.3.6 of ACI318),
• = 45 o
Required Area for Torsion Shear per Stirrups Spacing (According to Eq. 11-20, 21 of ACI318),
T u 12000
*
A' vt= = 0.025 in 2 per in
2* • * A o * f yt •* / 1 tan •• • •
s
Calculation of Shear Reinforcement
Nominal Shear Strength Provided by Concrete (According to Eq.11-3 of ACI318) •
*bd
V c= * •2 * • f'c * 1000 = 102.95 kips
Nominal Shear Strength Provided by Reinforcement (According to Eq.11-2 of ACI318) •
V s= V u/ • s • V c = 66.65 kips
Required Area for Direct Shear per Stirrups Spacing (According to Eq. 11-1, 2 of ACI318),
V s 1000
*
A' vs= = 0.024 in 2 per in
f yt d*
Interactive Design Aids for Structural Engineers
Chapter 1: Concrete Design ACI 318
Precast Spandrel Beam for Combined Shear and Torsion Page: 9
Calculation of Combined Shear and Torsion Reinforcement
Total Required Area for Torsion & Shear per Stirrups Spacing (According to Cl.11.5.3.8 of ACI318),
A' v= A' vt+ A' vs/ 2 = 0.037 in 2 per in per leg
Provided Reinforcement, Bar= SEL("ACI/Bar"; Bar; ) = No.4
Provided Reinforcement, A sb= TAB("ACI/Bar"; Asb; Bar=Bar) = 0.20 in 2
Required Stirrups Spacing, s_ Req= A sb/ A' v = 5.41 in
Provided Stirrups Spacing, s_ Prov= 5.00 in
Check Validity= IF(s_ Prov • s_ Req; " Valid"; "Invalid") = Valid
Perimeter of Stirrups, Ph= *2• -2
b co'
* + -2
h co'
* • + *2bL = 132.00 in
Maximum Stirrups Spacing Due to Torsion (According to Cl.11.6.6 of ACI318), s max_t=
MIN(Ph/8; 12) = 12.00 in
Maximum Stirrups Spacing Due to Shear (According to Cl.11.4.5 of ACI318), s max_v=
MIN(d/2; 24) = 22.75 in
Maximum Stirrups Spacing, s max= MIN(s max_t; s max_v) = 12.00 in
Check Validity= IF(s_ Prov • s max; " Valid"; "Invalid") = Valid
Calculation of Longitudinal Torsion Reinforcement
Required Area of Longitudinal Torsion Reinforcement (According to Cl.11.5.3.7 of ACI318),
*
A' vt Ph f yt
A l_i= * = 3.30 in 2
2 fy
tan • • •
Minimum Area of Longidudinal Torsion Reinforcement (According to Eq.11-24 of ACI318),
5*
• f' c A* cp
A l_min= - A' vt * Ph f*yt = 1.98 in 2
fy fy
A l_Req= MAX( A l_i ; A l_min) = 3.30 in 2
Provided Reinforcement, Bar= SEL("ACI/Bar"; Bar; ) = No.5
Provided Reinforcement, A sb= TAB("ACI/Bar"; Asb; Bar=Bar) = 0.31 in 2
Number of Bars, n= 12
Provided Longitudinal Reinforcement, A l_Prov= A sb * n = 3.72 in 2
Check Validity= IF(A l_Prov • A l_Req; " Valid"; "Invalid") = Valid
Interactive Design Aids for Structural Engineers
Chapter 1: Concrete Design ACI 318
Precast Spandrel Beam for Combined Shear and Torsion Page: 10
Calculation of Required Flexural Reinforcement
M u * 12 1000
*
R n= = 530 psi
• t
* *bd2
• ••
0.85 f' *c *2Rn
• =
fy
* -1 1
0.85 f' *c
• = 0.0095
Area of Flexural Reinforcement, A s= • * b*d = 6.92 in 2
Calculation of Total Bottom Reinforcement at Mid-Span
Percentage of Torsional Reinforcement Concentrated on Bottom Side, Per= 16 %
Total Area of Bottom Reinforcement at Mid-Span, A sc_Req=
A l_Req * / Per 100
+ As = 7.45 in 2
Provided Reinforcement, Bar= SEL("ACI/Bar"; Bar; ) = No.11
Provided Reinforcement, A sb= TAB("ACI/Bar"; Asb; Bar=Bar) = 1.56 in 2
Number of Bars, n= 5
Total Area of Bottom Reinforcement, A sc_Prov= A sb * n = 7.80 in 2
Check Validity= IF(A sc_Prov • A sc_Req; " Valid"; "Invalid") = Valid
Design Summary
Total Required Area for Torsion & Shear per Stirrups Spacing,
A' v= A' v = 0.037 in 2 per in per leg
Provided Stirrups Spacing, s_ Prov= s_ Prov = 5.00 in
Provided Longitudinal Reinforcement, A l_Prov= A l_Prov = 3.72 in 2
Total Area of Bottom Reinforcement, A sc_Prov= A sc_Prov = 7.80 in 2
Interactive Design Aids for Structural Engineers
Chapter 1: Concrete Design ACI 318
Beam Ledge Design Page: 11
Design of Beam Ledge as per ACI 318-11 Chapters 9 & 11
Beam Ledge Design
aS
Pu
co
h
L
d Lh L W
b bL bw
Ah Asc
System
Width of Beam, b= 7.0 in
Height of Beam, h= 36.0 in
Width of Beam Ledge, b L= 6.0 in
Height of Beam Ledge, h L= 12.0 in
Concrete Cover, co= 1.25 in
Width of Bearing Pad, W= 4.5 in
Length of Bearing Pad, L= 4.5 in
Thickness of Bearing Pad, t b= 0.3 in
Gap Spacing, a s= 1.0 in
Shear Spacing, a v= 2/3 * L + a s = 4.0 in
Flexural Spacing, a f= a v + co = 5.25 in
Effective Width According to Shear Requirements, b ws= W + 4 * a v = 20.5 in
Effective Width According to Flexural Requirements, b wf= W + 5 * a f = 30.8 in
Effective Depth of Beam Ledge, d L= -
h L co = 10.75 in
Load
Dead Load, P D= 11.0 kips
Live Load, P L= 6.5 kips
Service Load, P= PD+PL = 17.5 kips
Ultimate Load, P u= 1.2 * P D + 1.6 * P L = 23.6 kips
Interactive Design Aids for Structural Engineers
Chapter 1: Concrete Design ACI 318
Beam Ledge Design Page: 12
Material Properties
Concrete Strength, f' c= 5000 psi
Yield Strength of Reinforcement, f y= 60000 psi
Shear Strength Reduction Factor (According to Cl.9.3.2 of ACI318), • s= 0.75
Bearing Strength Reduction Factor (According to Cl.9.3.2 of ACI318), • b= 0.65
Modification Factor for Lightweight Concrete, •• • 1.00
Friction Factor (According to Cl.11.6.4.3 of ACI318), •= 1.4* • = 1.40
Maximum Service Load for Bearing Pads, q= 1000 psi
Check Bearing Plate Dimension
Capacity of Bearing Plate, B p= W * L * q /1000 = 20.25 kips
Check Validity= IF( B p> P;"Valid" ;"Increase Dimension" ) = Valid
Check Concrete Bearing Strength
Bearing Strength of Concrete, • P nb= • b
* 0.85 * f' c * L* /W
1000 = 55.9 kips
Check Validity= IF( • P nb> Pu;"Valid" ;"Invalid" ) = Valid
Check Maximum Nominal Shear-Transfer by Effective Section
Nominal Shear by Effective Section (According to Cl.11.9.3.2.1 of ACI318), V n1=
0.2 * f' c * b ws * d L / 1000 = 220.4 kips
V n2= (480 + 0.08 * f' c) * b ws * d L / 1000 = 193.9 kips
V n3= 1600 * b ws * d L / 1000 = 352.6 kips
• V n= • s* MIN(V n1; V n2; V n3) = 145.4 kips
Check Validity= IF( • V n> P u;" Valid" ;"Increase Dimension" ) = Valid
Determine Shear Friction Reinforcement (A vf)
Required Reinforcement for Shear Friction (According to Cl.11.6.4.1 of ACI318),
A vf= P u * 1000 / ( • s * f y * •) = 0.37 in 2 per bws
Determine Direct Tension Reinforcement (A n)
Required Reinforcement for Direct Tension (According to Cl.11.8.3.4 of ACI318),
A n= 0.2 * P u * 1000 / ( • s * f y) = 0.10 in 2 per bwf
Determine Flexural Reinforcement (A f)
M u= P u * a f + 0.2 * P u * ( h L - d L) = 129.8 kip*in
Required Reinforcement for Flexural (According to Cl.11.8.3.3 of ACI318),
A f= M u * 1000 / ( • s * f y * 0.8 * d L) = 0.34 in 2 per bwf
Interactive Design Aids for Structural Engineers
Chapter 1: Concrete Design ACI 318
Beam Ledge Design Page: 13
Determine Primary Tension Reinforcement (A sc)
Required Area of Reinforcement for Primary Tension (According to Cl.11.8.3.5 of ACI318),
A sc= MAX (2/3 * A vf/ b ws + A n/ b wf ; A f/ b wf + A n/ b wf) = 0.015 in 2 per in
Minimum Area of Reinforcement for Primary Tension (According to Cl.11.8.5 of ACI318), A sc_min=
0.04 * / f' c f *y d L = 0.036 in 2 per in
A sc_req= MAX (A sc; A sc_min) = 0.036 in 2 per in
Provided Reinforcement, Bar= SEL("ACI/Bar"; Bar; ) = No.5
Spacing between Bars, s= 8.0 in
Provided Reinforcement, A sb= TAB("ACI/Bar"; Asb; Bar=Bar) = 0.31 in 2
Check Validity= IF(A sb/ A sc_req> s; "Valid"; "Invalid") = Valid
Determine Horizontal Reinforcement (A h)
Required Area of Reinforcement for Horizontal Shear (According to Cl.11.8.4 of ACI318),
A h= 0.5*(A sc_req- A n/ b wf) = 0.016 in 2 per in
Provided Reinforcement, Bar= SEL("ACI/Bar"; Bar; ) = No.4
Provided Reinforcement, A sb= TAB("ACI/Bar"; Asb; Bar=Bar) = 0.20 in 2
Check Validity= IF(A sb/ A h> s; "Valid"; "Invalid") = Valid
Design Summary
Primary Tension Reinforcement, A sc_req= A sc_req = 0.036 in 2 per in
Horizontal Shear Reinforcement, A h= Ah = 0.016 in 2 per in
Distribute in two-thirds of Effective Ledge Depth adjacent to A sc
Interactive Design Aids for Structural Engineers
Chapter 1: Concrete Design ACI 318
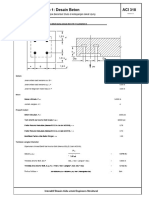
Rectangular Section with Tension Reinforcement Page: 14
Design of Rectangular Section with Tension Reinforcement only as per ACI 318-11 Chapters 9 & 10
Rectangular Section with Tension Reinforcement
•c
0.85 f'c
C
a a
c
N.A
d
h d-a/2
As
T
co •s
b
System
Width of Concrete Section, b= 12.0 in
Depth of Concrete Section, h= 16.0 in
Concrete Cover, co= 2.5 in
Effective Depth of Concrete Section, d= co- h = 16.0 2.5
- = 13.5 in
Load
Bending Moment due to Dead Load, M D= 56.0 kip*ft
Bending Moment due to Live Load, M L= 35.0 kip*ft
Ultimate Bending Moment, M U= • 1.2 M
*D • + • 1.6 M
*L • = 123.2 kip*ft
Material Properties
Concrete Strength, f' c= 4000 psi
Yield Strength of Reinforcement, f y= 60000 psi
Tension Strength Reduction Factor (According to Cl.9.3.2 of ACI318), •= 0.90
Factor for Rectangular Compressive Stress Block (According to Cl.10.2.7.3),
• 1=
IF(f' c • 4000;0.85;IF(f' c • 8000;0.65;1.05-0.00005*f' c)) = 0.85
Area of Reinforcement
M U 12000
*
R n= = 751.1 psi
• * *bd2
• = 0.85 f' *c
fy •
* -1 ••1
*2Rn
0.85 f' *c
• = 0.0143
Area of Reinforcement, A s= • * d* b = 2.32 in 2
Interactive Design Aids for Structural Engineers
Chapter 1: Concrete Design ACI 318
Rectangular Section with Tension Reinforcement Page: 15
Minimum Area of Reinforcement (According to Cl.10.5 of ACI318),
* 3 • f' c * *b
A s_min1= dfy = 0.51 in 2
200 ** b d f y
A s_min2= = 0.54 in 2
A s_min= MAX(A s_min1 ; A s_min2) = 0.54 in 2
Required Area of Reinforcement, A sc_Req= MAX(A s; A s_min) = 2.32 in 2
Provided Reinforcement, Bar= SEL("ACI/Bar"; Bar; ) = No.10
Provided Reinforcement, A sb= TAB("ACI/Bar"; Asb; Bar=Bar) = 1.27 in 2
Number of Bars, n= 2
Vertical Reinforcement, A sc_Prov= A sb * n = 2.54 in 2
Check Validity= IF(A sc_Prov • A sc_Req; " Valid"; "Invalid") = Valid
Check Tension Controlled
A sc_Prov *fy
Depth of Rectangular Stress Block, a= = 3.74 in
0.85 * f' c b*
Distance from Extreme Compression Fiber to Neutral Axis, c=a/ • 1 = 4.40 in
c/d = /
/ c d = 4.40 13.5 = 0.326
IF(c/d>0.375; "Add Com. RFT"; "Tension Controlled" ) = Tension Controlled
Design Summary
Required Area of Reinforcement, A sc= A sc_Prov = 2.54 in 2
Interactive Design Aids for Structural Engineers
Chapter 1: Concrete Design ACI 318
Rectangular Section with Compression Reinforcement Page: 16
Design of Rectangular Section with Compression Reinforcement as per ACI 318-11 Chapters 9 & 10
Rectangular Section with Compression Reinforcement
•c
0.85 f'c
d' C' s
As' • s' a
c Cc
N.A
dt d
h d-a/2
s
As
T
co •s
System
Width of Concrete Section, b= 12.0 in
Depth of Concrete Section, h= 32.5 in
Concrete Cover, co= 2.5 in
Effective Depth of Concrete Section to Extreme Layer , d t= co- h = 32.5 2.5
- = 30.0 in
Distance between C.G of Tension Reinforcement and Extreme Layer, s= 1.2 in
Effective Depth of Concrete Section to C.G of Tension Reinforcement, d= - dts= 28.8 in
Depth of Compression Reinforcement, d'= 2.5 in
Load
Bending Moment due to Dead Load, M D= 430.0 kip*ft
Bending Moment due to Live Load, M L= 175.0 kip*ft
Ultimate Bending Moment, M U= • 1.2 M
*D • + • 1.6 M
*L • = 796.0 kip*ft
Material Properties
Concrete Strength, f' c= 4000 psi
Yield Strength of Reinforcement, f y= 60000 psi
Modulus of Elasticity of Reinforcement, E s= 29000000 psi
Tension Strength Reduction Factor (According to Cl.9.3.2 of ACI318), •= 0.90
Factor for Rectangular Compressive Stress Block (According to Cl.10.2.7.3),
• 1=
IF(f' c • 4000;0.85;IF(f' c • 8000;0.65;1.05-0.00005*f' c)) = 0.85
Interactive Design Aids for Structural Engineers
Chapter 1: Concrete Design ACI 318
Rectangular Section with Compression Reinforcement Page: 17
Check If Compression Reinforcement is Required
• t=
0.31875* • 1 = 0.271
R nt= • t*( 1-0.59* • t)* f' c = 910.7 pci
M U 12000
*
R n= = 982.7 psi
2
• * d t* b
Compression Reinforcement is: IF(R n> R nt;" Required";"Not Required") = Required
Determine Required Moment Resisted by Compression Reinforcement
• t=
0.31875* • 1 = 0.271
• t=
0.31875 * f' c * • 1 / f y = 0.01806
• = • t* d t/ d = 0.01881
• = • * f y/ f' c = 0.28215
f' c * *bd2
Moment Resisted by Tension RFT, M nt= • *•1 - 0.59 • * • * = 780.3 kip*ft
12000
Moment Resisted by Compression RFT, M' n= M U/ ••• M nt = 104.1 kip*ft
Required Area of Compression Reinforcement
fy
d'/c limit= 1 - = 0.31
*
E s 0.003
•fy •
c limit=
• 1 -
E s 0.003
* dt • * = 9.3 in
c cal= 0.375*d t = 11.3 in
d'/c cal= • / d' c cal • = 0.22
f' si= MIN(0.003*E s*( 1- d'/c cal); f y ) = 60000 psi
f' s= IF(d'/c cal • d'/c limit; f y ; f' si ) = 60000 psi
M' n 12000
*
Required Reinforcement Area for Compression, A' s= = 0.79 in 2
f' s •* d' - d •
Provided Reinforcement, Bar= SEL("ACI/Bar"; Bar; ) = No.6
Provided Reinforcement, A sb= TAB("ACI/Bar"; Asb; Bar=Bar) = 0.44 in 2
Number of Bars, n= 2
Vertical Reinforcement, A' s_Prov= A sb * n = 0.88 in 2
Check Validity= IF(A' s_Prov • A' s; " Valid"; "Invalid") = Valid
Required Reinforcement Area for Tension, A s= A' s + ( •• b*d) = 7.29 in 2
Interactive Design Aids for Structural Engineers
Chapter 1: Concrete Design ACI 318
Rectangular Section with Compression Reinforcement Page: 18
Minimum Area of Reinforcement (According to Cl.10.5 of ACI318),
* 3 • f' c * *b
A s_min1= dfy = 1.09 in 2
200 ** b d f y
A s_min2= = 1.15 in 2
A s_min= MAX(A s_min1 ; A s_min2) = 1.15 in 2
Required Area of Reinforcement, A sc_Req= MAX(A s; A s_min) = 7.29 in 2
Provided Reinforcement, Bar= SEL("ACI/Bar"; Bar; ) = No.10
Provided Reinforcement, A sb= TAB("ACI/Bar"; Asb; Bar=Bar) = 1.27 in 2
Number of Bars, n= 6
Vertical Reinforcement, A sc_Prov= A sb * n = 7.62 in 2
Check Validity= IF(A sc_Prov • A sc_Req; " Valid"; "Invalid") = Valid
Design Summary
Required Reinforcement Area for Compression, A' s= A' s_Prov = 0.88 in 2
Required Area of Reinforcement, A sc= A sc_Prov = 7.62 in 2
Interactive Design Aids for Structural Engineers
Chapter 1: Concrete Design ACI 318
Shear Reinforcement for Section Subject to Q & N Page: 19
Design of Shear Reinforcement for Section Subject to Shear & Axial Compression As per ACI318-11
Shear Reinforcement for Section Subject to Q & N
Av
d Nu
co h Vu
b
s
System
Width of Concrete Section, b= 12.0 in
Depth of Concrete Section, h= 16.0 in
Concrete Cover, co= 2.25 in
Effective Depth of Concrete Section, d= co- h = 13.75 in
Load
Shear Force due to Dead Load, V D= 10.0 kips
Shear Force due to Live Load, V L= 5.0 kips
Ultimate Shear Force, V u= • 1.2 V* D • + • 1.6 V* L • = 20.0 kips
Axial Compression Force due to Dead Load, N D= 4.2 kips
Axial Compression Force due to Live Load, N L= 3.1 kips
Ultimate Axial Compression Force, N u= • 1.2 N* D • + • 1.6 N* L • = 10.0 kips
Material Properties
Concrete Strength, f' c= 4000 psi
Yield Strength of Reinforcement, f y= 60000 psi
Shear Strength Reduction Factor (According to Cl.9.3.2 of ACI318), •= 0.75
Modification Factor for Lightweight Concrete, •• • 1.00
Interactive Design Aids for Structural Engineers
Chapter 1: Concrete Design ACI 318
Shear Reinforcement for Section Subject to Q & N Page: 20
Determine Concrete Shear Strength
Nominal Shear Strength provided by Concrete (According to Eq. 11-4 of ACI318),
• •
N u 1000
* f' c * *b
V c= *2 1 +
2000 * * h b
• *• * d 1000 = 21.4 kips
Shear Reinforcement is : IF(V u> •• V c;" Required";"Not Required") = Required
Determine Area of Shear Reinforcement
Nominal Shear Strength provided by Reinforcement (According to Eq. 11-2 of ACI318),
Vu -• * Vc
V s= = 5.3 kips
•
Maximum Allowable Shear Strength provided by Reinforcement (According to Cl.11.4.7.9 of ACI318),
f' c * *b
•
V s_max= * •8 * d 1000 = 83.5 kips
IF(V s> V s_max; " Increase Beam Dimension"; "OK" ) = OK
Spacing of Provided Stirrups, s= 6.75 in
Vs * * s 1000
Required Area of Reinforcement, A v= = 0.04 in 2
*fyd
Minimum Area of Reinforcement (According to Cl.11.4.6.3 of ACI318),
0.75 • *f' c * *b
A v_min1= sfy = 0.06 in 2
50 ** b s f y
A v_min2= = 0.07 in 2
A v_min= MAX(A v_min1 ; A v_min2) = 0.07 in 2
Required Area of Reinforcement, A vc_Req= MAX(A v; A v_min) = 0.07 in 2
Provided Reinforcement, Bar= SEL("ACI/Bar"; Bar; ) = No.3
Provided Reinforcement, A sb= TAB("ACI/Bar"; Asb; Bar=Bar) = 0.11 in 2
Number of Stirrups, n= 1
Provided Area of Reinforcement, A vc_Prov= A sb * n * 2 = 0.22 in 2
Check Validity= IF(A vc_Prov • A vc_Req; " Valid"; "Invalid") = Valid
Interactive Design Aids for Structural Engineers
Chapter 1: Concrete Design ACI 318
Shear Reinforcement for Section Subject to Q & N Page: 21
Determine Maximum Permissible Spacing of Stirrups
Allowable Shear Strength provided by Reinforcement for Spacing Limit (According to Cl.11.4.5.3 of ACI318), V s_limit=
* •4 * f' c * b * / d 1000
• = 41.7 kips
Factor for Maximum Spacing of Stirrups, Fac=IF(V s • V s_limit; 1;0.5) = 1.0
Maximum Spacing of Stirrups (According to Cl.11.4.5.1 of ACI318), s max=
MIN(d/2;24 ) * Fac = 6.88 in
Check Validity= IF(s • s max;" Valid"; "Invalid") = Valid
Design Summary
Provided Area of Shear Reinforcement, A vc_Prov= A vc_Prov = 0.22 in 2
Spacing of Stirrups, s= s = 6.75 in
Interactive Design Aids for Structural Engineers
Chapter 1: Concrete Design ACI 318
Shear Reinforcement for Section Subject to Q & T Page: 22
Design of Shear Reinforcement for Section Subject to Shear & Axial Tension As per ACI318-11
Shear Reinforcement for Section Subject to Q & T
Av
d Nu
co h Vu
b
s
System
Width of Concrete Section, b= 10.5 in
Depth of Concrete Section, h= 18.0 in
Concrete Cover, co= 2.0 in
Effective Depth of Concrete Section, d= - h co = 16.0 in
Load
Shear Force due to Dead Load, V D= 12.8 kips
Shear Force due to Live Load, V L= 9.0 kips
Ultimate Shear Force, V u= • 1.2 V* D • + • 1.6 V* L • = 29.8 kips
Axial Tension Force due to Dead Load, N D= - 2.0 kips
Axial Tension Force due to Live Load, N L= - 15.2 kips
Ultimate Axial Tension Force, N u= • 1.2 N* D • + • 1.6 N* L • = - 26.7 kips
Material Properties
Concrete Strength, f' c= 3600 psi
Yield Strength of Reinforcement, f y= 40000 psi
Shear Strength Reduction Factor (According to Cl.9.3.2 of ACI318), •= 0.75
Modification Factor for Lightweight Concrete, •• • 0.85
Determine Concrete Shear Strength
Nominal Shear Strength provided by Concrete (According to Eq. 11-8 of ACI318),
• •
N u 1000
* f' c * *b
V c= *2 1 +
500 ** h b
• *• * d 1000 = 12.3 kips
Shear Reinforcement is : IF(V u> •• V c;" Required";"Not Required") = Required
Interactive Design Aids for Structural Engineers
Chapter 1: Concrete Design ACI 318
Shear Reinforcement for Section Subject to Q & T Page: 23
Determine Area of Shear Reinforcement
Nominal Shear Strength provided by Reinforcement (According to Eq. 11-2 of ACI318),
Vu -• * Vc
V s= = 27.4 kips
•
Maximum Allowable Shear Strength provided by Reinforcement (According to Cl.11.4.7.9 of ACI318),
f' c * *b
•
V s_max= * •8 * d 1000 = 68.5 kips
IF(V s> V s_max; " Increase Beam Dimension"; "OK" ) = OK
Spacing of Provided Stirrups, s= 5.0 in
Vs * * s 1000
Required Area of Reinforcement, A v= = 0.21 in 2
*fyd
Minimum Area of Reinforcement (According to Cl.11.4.6.3 of ACI318),
0.75 • *f' c * *b
A v_min1= sfy = 0.06 in 2
50 ** b s f y
A v_min2= = 0.07 in 2
A v_min= MAX(A v_min1 ; A v_min2) = 0.07 in 2
Required Area of Reinforcement, A vc_Req= MAX(A v; A v_min) = 0.21 in 2
Provided Reinforcement, Bar= SEL("ACI/Bar"; Bar; ) = No.3
Provided Reinforcement, A sb= TAB("ACI/Bar"; Asb; Bar=Bar) = 0.11 in 2
Number of Stirrups, n= 1
Provided Area of Reinforcement, A vc_Prov= A sb * n * 2 = 0.22 in 2
Check Validity= IF(A vc_Prov • A vc_Req; " Valid"; "Invalid") = Valid
Determine Maximum Permissible Spacing of Stirrups
Allowable Shear Strength provided by Reinforcement for Spacing Limit (According to Cl.11.4.5.3 of ACI318),
f' c * *b
•
V s_limit= * •4 * d 1000 = 34.3 kips
Factor for Maximum Spacing of Stirrups, Fac= IF(V s • V s_limit; 1;0.5) = 1.0
Maximum Spacing of Stirrups (According to Cl.11.4.5.1 of ACI318), s max=
MIN(d / 2;24 ) * Fac = 8.00 in
Check Validity= IF(s • s max;" Valid"; "Invalid") = Valid
Design Summary
Provided Area of Shear Reinforcement, A vc_Prov= A vc_Prov = 0.22 in 2
Spacing of Stirrups, s= s = 5.00 in
Interactive Design Aids for Structural Engineers
Chapter 1: Concrete Design ACI 318
Deflection of Shored Composite Section Page: 24
Calculation of Deflection of Shored Nonprestressed Simple Support Concrete Composite Section As per ACI318-11 Chapter 9
Deflection of Shored Composite Section
be
hf
Cast in Situ Slab
h Precast Beam
As
co
System
Beam Span, L= 26.0 ft
Beam Spacing, S= 8.0 ft
Width of Precast Beam, b= 12.0 in
Depth of Precast Beam, h= 20.0 in
Thickness of Cast in Situ Slab, h f= 4.0 in
Area of Tension Reinforcement for Precast Beam, A s= 3.00 in 2
Concrete Cover for Precast Beam, co= 2.5 in
Effective Width of Slab, b e1= L*12 / 4 = 78.0 in
Effective Width of Slab, b e2= S*12 = 96.0 in
Effective Width of Slab, b e3= 16*hf + b = 76.0 in
Effective Width of Slab, b e= MIN(b e1; b e2; b e3) = 76.0 in
Material Properties
Concrete Strength of Cast in Situ Slab, f' c1= 3000 psi
Concrete Strength of Precast Beam, f' c2= 4000 psi
Yield Strength of Reinforcement, f y= 40000 psi
Modulus of Elasticity of Reinforcement, E s= 29000000 psi
Modification Factor for Lightweight Concrete, •• • 1.00
Concrete Density, w c= 150 psi
Interactive Design Aids for Structural Engineers
Chapter 1: Concrete Design ACI 318
Deflection of Shored Composite Section Page: 25
Load
Superimposed Dead Load, SDL= 10.00 psf
Live Load, LL= 75.00 psf
Dead Load per Unit Length for Slab, w d1= SDL*S + w c* S*12*h f/ 144 = 480.0 Ib/ft
Dead Load per Unit Length for Beam, w d2= w c* b*h/144 = 250.0 Ib/ft
Live Load per Unit Length, w l= LL*S = 600.0 Ib/ft
Percentage of Sustained Live Load, Sus= 20 %
Bending Moment of Dead Load 1, M D1= 1/1000 * w d1* L 2/ 8 = 40.6 kip*ft
Bending Moment of Dead Load 2, M D2= 1/1000 * w d2* L 2/ 8 = 21.1 kip*ft
Bending Moment of Live Load, M L= 1/1000 * w l* L 2/ 8 = 50.7 kip*ft
Bending Moment of Sustained Load, M sus= M D1 + M D2 + ( Sus/100) * M L = 71.8 kip*ft
Calculation of Modular Ratio
For Cast in Situ Slab:
Modulus of Elasticity of Concrete (According to Cl. 8.5.1 of ACI318),
1.5
E c1= wc * 33 •* f' c1 = 3320561 psi
7.5 ** • f' c1
Modulus of rupture (According to Eq. 9-10 of ACI318), f r1=
• = 411 psi
For Precast Beam:
Modulus of Elasticity of Concrete (According to Cl. 8.5.1 of ACI318),
1.5
E c2= wc * 33 •* f' c2 = 3834254 psi
7.5 ** • f' c2
Modulus of rupture (According to Eq. 9-10 of ACI318), f r2=
• = 474 psi
n c= E c2 / E c1 = 1.15
n s= E s / E c2 = 7.56
Width of Slab considering relative Concrete Strength, bs= be/n c = 66.09 in
Calculation of Moment of Inertia for Cracked Section
For Precast Beam
Effective Depth of Section, d= 17.5 in
I g1= b*h 3/ 12 = 8000 in 4
B= b/(n s* A s) = 0.53 1/in
• *d
2+* B 1 1 B-
kd= = 6.5 in
* b kd 3
I cr1= + n s * A s •* - d kd•2 = 3842.8 in 4
3
Interactive Design Aids for Structural Engineers
Chapter 1: Concrete Design ACI 318
Deflection of Shored Composite Section Page: 26
For Composite Section
Effective Depth of Section, d= (h+hf) - co = 21.5 in
h1 = h + hf = 24.0 in
bs1 = bs - b = 54.1 in
Distance from Centroidal Axis of Gross Section to Tension Face,
1 bs1 hf* 2 + * b h1 2
yt= h1 *- = 16.3 in
2 bs1 +* hf h1
*b
2 2
• •*
bs1 hf* 3 * b h1 3 hf 2 yt
I g2=
12
+
12
+ bs1 * * hf h + -
• + b * h1 -
yt h1
2
• = 26468.49 in 4
B= bs • / *
n s As • = 2.91 1/in
• 2* d * + B 1- 1
kd= B = 3.5 in
bs kd
* 3
I cr2= + n s * As • * - d kd•2 = 8292.9 in 4
3
I g1 I cr1
Ratio between Cracking & Gross Inertia, r=
•I g2
+
I cr2 • /2 = 0.383
Cracking Moment (According to Eq. 9-9 of ACI318),
f r2 I*g1
Cracking Moment for Beam Section, M cr1= = 31.60 kip*ft
/ h 2* 12000
f r2 I*g2
Cracking Moment for Beam Section, M cr2= = 64.14 kip*ft
yt 12000
*
Effective Moment of Inertia for Composite Section,
3
3
• • ••
M cr1
• •
M cr1
I e1,2= * I g1 + -1 * I cr1 = 4401 in 4
M D1 M+D2 M D1 M+D2
3
3
• • ••
M cr2
• •
M cr2
I ed,l= * I g2 + -1 * I cr2 = 11670 in 4
M D1 + M D2 M+L
M D1 + M D2 M+L
Check Validity= IF(I e1.2< I g1; " Valid"; "Invalid") = Valid
Short Term Deflection
Short Term Deflection of composite section Due to Dead Load,
5* • M D1 M+D2 • * L 2 12
* 3
• i1,2=
= 0.074 in
48 * E c2 I g2 /
* 1000
Interactive Design Aids for Structural Engineers
Chapter 1: Concrete Design ACI 318
Deflection of Shored Composite Section Page: 27
Deflection Due to Shrinkage
For Simple Span, Ksh= 0.125
*
A s 100
• = = 1.16 %
d *b
(According to Fig.10-3 of PCA Note on ACI318), Ash= 0.789
Time Dependant Shrinkage Strain, • sht= 400 10-
* 6 = 0.00040
Deflection Due to Shrinkage, • sh= 0.64 * Ksh * Ash * • sht L*2 12 2* * /rh= 0.047 in
Deflection Due to Creep
For No Compression Reinforcement Factor of, k r= 0.85
Average Creep Coefficient (According to Cl.2.3.4 of ACI435), Cu= 1.67
Deflection Due to Creep, • cp= Cu * • *
i1,2 k r
= 0.105 in
Deflection Due to Live Load
5* • M D1 + M D2 M+L • * L 2 12
* 3
Deflection Due to Live Load , • L= - • i1,2 = 0.232 in
48 * E c2 I ed,l /
* 1000
Deflection Due to Creep Sustained Live Load, • cp, L= Cu Sus
* *• *
Lkr
= 0.066 in
100
Total Long Term Deflection
Total Deflection, • u= • *
i1,2 3.53
+• sh
+ • cp • +L = 0.65 in
Calculation Summary
Total Deflection, • u= • *
i1,2 3.53
+• sh
+ • cp • +L = 0.65 in
Interactive Design Aids for Structural Engineers
Chapter 1: Concrete Design ACI 318
Flexural Design of Flanged Section Page: 28
Design of Flanged Section with Tension Reinforcement only as per ACI 318-11 Chapters 9 & 10
Flexural Design of Flanged Section
bf bf
a hf hf
a
d As d As
h h
co co
bw bw
Design as Rectangular Section Design as Flanged Section
System
Width of Concrete Flange, b f= 30.0 in
Width of Concrete Web, b w= 10.0 in
Depth of Concrete Section, h= 20.0 in
Thickness of Top Flange, h f= 2.5 in
Concrete Cover, co= 1.0 in
Effective Depth of Concrete Section, d= co- h = 20.0 1.0
- = 19.0 in
Load
Bending Moment due to Dead Load, M D= 72.0 kip*ft
Bending Moment due to Live Load, M L= 196.0 kip*ft
Ultimate Bending Moment, M U= • 1.2 M
*D • + • 1.6 M
*L • = 400.0 kip*ft
Material Properties
Concrete Strength, f' c= 4000 psi
Yield Strength of Reinforcement, f y= 60000 psi
Tension Strength Reduction Factor (According to Cl.9.3.2 of ACI318), •= 0.90
Factor for Rectangular Compressive Stress Block (According to Cl.10.2.7.3 of ACI318),
• 1=
IF(f' c • 4000;0.85;IF(f' c • 8000;0.65;1.05-0.00005*f' c)) = 0.85
Interactive Design Aids for Structural Engineers
Chapter 1: Concrete Design ACI 318
Flexural Design of Flanged Section Page: 29
Design as Flanged Section
b f b- w
Compressive Strength of Flange, C f= 0.85 * f' c h* f * = 170.0 kips
1000
Cf
Area of Reinforcement for Flange in Compression, A sf= * 1000 = 2.83 in 2
fy
A sf * f y
•
hf
Nominal Moment for Flange, M nf=
12000 • * -d
2
= 251.2 kip*ft
Nominal Moment for Web, M nw= / M U- • M nf = 193.24 kip*ft
M nw 12000
*
R nw= = 713.7 psi
• * b w d *2
• w=
0.85 * / f' c f y* • •• -1 1
* 2 R nw
0.85 f' *c
• = 0.0135
Area of Reinforcement for Web in Compression, A sw= • w * b w * d = 2.56 in 2
Required Area of Reinforcement, A s_T= A sf + A sw = 5.39 in 2
A sw f y*
Depth of Rectangular Stress Block for Web, a w= = 4.52 in
0.85 * f' c b* w
Design as Rectangular Section
M U 12000
*
R n= = 492.46 psi
• * b f d*2
• = 0.85 f' *c
fy •* -1 •• 1
*2Rn
0.85 f' *c
• = 0.0089
Area of Reinforcement, A s_R= • •* b f * d = 5.07 in 2
A s_R f y*
Depth of Rectangular Stress Block, a= = 2.98 in
0.85 * f' c b* f
Interactive Design Aids for Structural Engineers
Chapter 1: Concrete Design ACI 318
Flexural Design of Flanged Section Page: 30
Section Type and Reinforcement
Section Design as: IF(a>h f; " Flanged Sec."; "Rectangular Sec." ) = Flanged Sec.
Area of Reinforcement, A s= IF(a>h f; A s_T; A s_R ) = 5.39 in 2
Minimum Area of Reinforcement (According to Cl.10.5 of ACI318),
f' c * b f d*fy
3*
•
A s_min1= = 1.80 in 2
200 * b f d*fy
A s_min2= = 1.90 in 2
A s_min= MAX(A s_min1 ; A s_min2) = 1.90 in 2
Required Area of Reinforcement, A sc_Req= MAX(A s; A s_min) = 5.39 in 2
Provided Reinforcement, Bar= SEL("ACI/Bar"; Bar; ) = No.10
Provided Reinforcement, A sb= TAB("ACI/Bar"; Asb; Bar=Bar) = 1.27 in 2
Number of Bars, n= 5
Vertical Reinforcement, A sc_Prov= A sb * n = 6.35 in 2
Check Validity= IF(A sc_Prov • A sc_Req; " Valid"; "Invalid") = Valid
Check Tension Controlled
Distance from Extreme Compression Fiber to Neutral Axis, c=
IF(a>h f; a w/ • 1; a/ • 1 ) = 5.32 in
c/d = /
/ c d = 5.32 19.0 = 0.280
IF(c/d>0.375; "Add Com. RFT"; "Tension Controlled" ) = Tension Controlled
Design Summary
Required Area of Reinforcement, A sc= A sc_Prov = 6.35 in 2
Interactive Design Aids for Structural Engineers
Chapter 1: Concrete Design ACI 318
Cracking Moment Strength for Prestressed Sections Page: 31
Cracking Moment Strength for Prestressed Sections as per ACI 318-11 Chapter 18
Cracking Moment Strength for Prestressed Sections
d
h
n.As
co
System
Width of Concrete Section, b= 12.0 in
Depth of Concrete Section, h= 24.0 in
Concrete Cover, co= 2.0 in
Effective Depth of Concrete Section, d= co- h = 24.0 2.0
- = 22.0 in
Number of Strands, n= 6.0
Area of One Strand, A s= 0.153 in 2
Material Properties
Concrete Strength, f' c= 5000 psi
Tensile Strength of Prestressed Steel, f pu= 270000 psi
Jacking Stress, J s= 0.7 * f pu = 189000 psi
Percentage of Losses, L s= 20.00 %
Modification Factor for Lightweight Concrete, •• • 1.00
7.5 ** •
Modulus of Rupture (According to Eq. 9-10 of ACI318), f r=
• f' c = 530 psi
Calculation of Cracking Moment Strength
Area of Concrete, A c= b*h = 288.0 in 2
Concrete Section Modulus, S b= b*h2/6 = 1152.0 in 3
Eccentricity of Prestressing, e= h/2 - co = 10.0 in
Effective Prestress Force, P se= (1-L s/ 100) * n * A s * J s / 1000 = 138.8 kips
fr P se Sb
• •
e
Cracking Moment Strength, M cr= + * + P se * = 212.8 kip*ft
1000 Ac 12 12
Calculation Summary
Cracking Moment Strength, M cr= M cr = 212.8 kip*ft
Interactive Design Aids for Structural Engineers
Chapter 1: Concrete Design ACI 318
Flexural Strength of Prestressed Member Page: 32
Flexural Strength of Prestressed Member Using Approximate Value of f ps As per ACI 318-11
Flexural Strength of Prestressed Member
d
h
n.As
co
System
Width of Concrete Section, b= 12.0 in
Depth of Concrete Section, h= 24.0 in
Concrete Cover, co= 2.0 in
Effective Depth of Concrete Section, d= co- h = 24.0 2.0
- = 22.0 in
Number of Strands, n= 6
Area of One Strand, A s= 0.153 in 2
Material Properties
Concrete Strength, f' c= 5000 psi
Tensile Strength of Prestressed Steel, f pu= 270000 psi
Yield Strength of Prestressed Steel, f py= 0.9 * f pu = 243000 psi
Factor for Type of Prestressing Steel (According to Cl.18.7.2 of ACI318), • p= 0.28
Factor for Rectangular Compressive Stress Block (According to Cl.10.2.7.3 of ACI318),
• 1=
IF(f' c • 4000;0.85;IF(f' c • 8000;0.65;1.05-0.00005*f' c)) = 0.80
Interactive Design Aids for Structural Engineers
Chapter 1: Concrete Design ACI 318
Flexural Strength of Prestressed Member Page: 33
Calculation of Stress for Prestressed Reinforcement
Prestressed Reinforcement Ratio, • p= n * A s / ( b * d) = 0.00348
Prestressing Force (According to Eq. 18-1 of ACI318),
f pu •p f pu
f ps=
1000 • * 1 -
•1
*• p *
f' c • = 252 ksi
Calculation of Nominal Moment Strength
* n A s* f ps
Distance of Compression Block, a= = 4.54 in
0.85 * *b / f' c 1000
* n A s* f ps a
Nominal Moment Strength, M n=
12
*
• -d
2
• = 380.4 kip*ft
Calculation Summary
Nominal Moment Strength, M n= Mn = 380.4 kip*ft
Interactive Design Aids for Structural Engineers
Chapter 1: Concrete Design ACI 318
Tension Controlled Limit for Prestressed Flexural Member Page: 34
Tension Controlled Limit for Prestressed Flexural Member as per ACI 318-11 Chapters 10 & 18
Tension Controlled Limit for Prestressed Flexural Member
hf
b
d
h d p
co p
b w/2 b w/2
co
System
Width of Concrete Double Tee Section, b= 84.0 in
Width of Web of Concrete Double Tee Section, b w= 15.5 in
Depth of Concrete Double Tee Section, h= 32.0 in
Thickness of Concrete Top Slab, h f= 2.0 in
Concrete Cover, co= 2.0 in
Concrete Cover to CG of Prestressed Steel, co p= 4.5 in
Effective Depth of Concrete Section, d= co- h = 30.0 in
Effective Depth of Concrete Section, d p= - h co p = 27.5 in
Number of Strands, n= 22.0
Area of One Strand, A s= 0.153 in 2
Material Properties
Concrete Strength, f' c= 5000 psi
Tensile Strength of Prestressed Steel, f pu= 270000 psi
Yield Strength of Prestressed Steel, f py= 0.9 * f pu = 243000 psi
Factor for Type of Prestressing Steel (According to Cl.18.7.2 of ACI318), • p= 0.28
Factor for Rectangular Compressive Stress Block (According to Cl.10.2.7.3 of ACI318),
• 1=
IF(f' c • 4000; 0.85; IF(f' c • 8000; 0.65; 1.05-0.00005*f' c)) = 0.80
Interactive Design Aids for Structural Engineers
Chapter 1: Concrete Design ACI 318
Tension Controlled Limit for Prestressed Flexural Member Page: 35
Calculation of Stress in Prestressed Reinforcement
• pu=
(n * A s) * f pu / ( b * d p * f' c) = 0.079
Prestressing Force (According to Eq.18-1 of ACI318),
f ps= f pu •
* 1 -
•p
• 1
*• pu • = 262535 psi
Area of Reinforcement for Compression in Flange,
A pf= 0.85 * h f * f' c * ( b-b w) / f pu = 2.16 in 2
Calculation of Depth of Concrete Stress Block
a i= (n * A s) * f ps / ( 0.85 * b * f' c) = 2.48 in
For a i > h f:
a 1= (n * A s - A pf) * f ps / ( 0.85 * b w * f' c) = 4.81 in
For a i • h f:
a 2= ai = 2.48 in
a= IF(a i> h f ; a 1 ; a 2) = 4.81 in
c= a/•1 = 6.01 in
Check Tension Controlled
c/d = c/d = 0.200
IF(c/d>0.375; "Compression Controlled"; "Tension Controlled" ) = Tension Controlled
Calculation Summary
Type of Section:
IF(c/d>0.375; "Compression Controlled"; "Tension Controlled" ) = Tension Controlled
Interactive Design Aids for Structural Engineers
Chapter 1: Concrete Design ACI 318
Prestress Losses Page: 36
Estimating Prestress Losses as per ACI 318-11 Chapter 18
Prestress Losses
y
t N.A
h
y
b
System
Area of Concrete Section, A c= 449 in 2
Depth of Concrete Section, h= 24 in
Concrete Cover, co= 2 in
Effective Depth of Concrete Section, d= co- h = 22 in
Moment of Inertia for Concrete Section, I c= 22469 in 4
Distance from Bottom Fiber to Neutral Axis, y b= 17.77 in
Distance from Top Fiber to Neutral Axis, y t= -hyb = 6.23 in
Number of Strands, n= 8.0
Area of One Strand, A s= 0.153 in 2
Eccentricity of Strands, e= 9.77 in
Volume per Surface Area, V.S= 1.35 in
Average Relative Humidity, RH= 75.00 %
Load
Factored Moment due to Dead Load, M D= 1617 kip*in
Factored Moment due to Superimposed Dead Load, M SD= 691 kip*in
Factored Moment due to Live Load, M L= 1382.00 kip*in
Interactive Design Aids for Structural Engineers
Chapter 1: Concrete Design ACI 318
Prestress Losses Page: 37
Material Properties
Concrete Strength, f' ci= 3500 psi
Concrete Strength, f' c= 5000 psi
Tensile Strength of Prestressed Steel, f pu= 270000 psi
Yield Strength of Prestressed Steel, f py= 0.9 * f pu = 243000 psi
Jacking Stress, J s= 0.74 * f pu = 199800 psi
Modification Factor for Lightweight Concrete, •• • 1.00
7.5 ** • f' c =
Modulus of Rupture (According to Eq. 9-10 of ACI318), f r=
• 530 psi
Concrete Density, w c= 150 psi
Modulus of Elasticity of Concrete (According to Cl. 8.5.1 of ACI318),
1.5
Modulus of Elasticity for Initial Concrete, E ci= wc * 33 •* f' ci = 3586616 psi
1.5
Modulus of Elasticity for Concrete, E c= wc * 33 •* f' c = 4286826 psi
Modulus of Elasticity of Prestressed Steel, E s= 28500000 psi
Calculation of Losses
1- Elastic Shortening of Concrete (ES) Initial Force of
Prestress, P pi= J s * ( n * A s)/ 1000 = 244.6 kips
Prestress Type= SEL("ACI/Kes" ;Type; ) = Pretensioned
K es= TAB("ACI/Kes" ;Kes ;Type=Type ) = 1.00
K cir= TAB("ACI/Kcir" ;Kcir ;Type=Type ) = 0.90
• P pi P pi M D e*I c
f cir= K cir *
Ac
+
Ic
* e2
• - = 0.722 ksi
Elastic Shortening of Concrete, ES= K es * E s * / f cir E ci = 5.74 ksi
2- Creep of Concrete (CR) Prestress
Type= SEL("ACI/Kcr" ;Type; ) = Pretensioned
Factor of, Kcr= TAB("ACI/Kcr" ;Kcr ;Type=Type ) = 2.00
Es eIc
Creep Losses, CR= K cr *
Ec •
* f cir - M SD *
• = 5.61 ksi
3- Shrinkage of Concrete (SH) Prestress
Type= SEL("ACI/Ksh" ;Type; ) = Pretensioned
Factor of, K sh= TAB("ACI/Ksh" ;Ksh ;Type=Type ) = 1.00
Es
Shrinkage Losses, SH= 8.2 * 10- 6 * K sh * *•1 - * •
0.06 V.S • -
* 100 RH • = 5.37 ksi
1000
Interactive Design Aids for Structural Engineers
Chapter 1: Concrete Design ACI 318
Prestress Losses Page: 38
4- Relaxation of Tendon (RE) Prestress
Type= SEL("ACI/KreJ" ;Type; ) = relaxation strand-Grade Low 270
Factor of, K re= TAB("ACI/KreJ" ;Kre ;Type=Type ) = 5000 psi
Factor of, J= TAB("ACI/KreJ" ;J ;Type=Type ) = 0.04
Ratio of f pi/ f pu, r= SEL("ACI/r" ;r; ) = 0.74
Factor of, C= TAB("ACI/r" ;C ;r=r ) = 0.95
K re
Relaxation of Tendon, RE=
•1000 * - J• SH + CR ES
+ C •
•* = 4.11 ksi
5- Total Allowance of Losses and Effective Prestress Force after all Losses Total Allowance of Losses, L s=
ES + CR + SH RE
+ = 21 ksi
Effective Prestress Stress, f se= / J s 1000- L s = 179 ksi
Effective Prestress Force after All Losses, P e= fse • * * n A s• = 219 kips
Calculation Summary
Total Allowance of Losses, L s= Ls = 21 ksi
Effective Prestress Force after All Losses, P e= P e = 219 kips
Interactive Design Aids for Structural Engineers
Chapter 1: Concrete Design ACI 318
Punching Shear Reinforcement on Slab Page: 39
Design Shear Reinforcement for Slab which to resist Punching Stress around Interior Square Column As per ACI318-11 Chapter 11
Punching Shear Reinforcement on Slab
2d
a√2
b1
d/2 c d/2
• Vc/2
d/2
Critical Section for Punching s
Shear Action
a c
System
Column Dimension, c= 12.0 in
Thickness of Concrete Slab, h= 7.5 in
Concrete Cover, co= 1.5 in
Effective Depth of Concrete Section, d= co- h = 7.5 1.5
- = 6.0 in
Bar Diameter of Shear Reinforcement, Dia= 0.375 in
Load
Ultimate Shear Force, V u= 120.0 kips
Material Properties
Concrete Strength, f' c= 4000 psi
Yield Strength of Reinforcement, f y= 60000 psi
Shear Strength Reduction Factor (According to Cl.9.3.2 of ACI318), •= 0.75
Modification Factor for Lightweight Concrete, •• • 1.00
Determine Concrete Shear Strength
b 1= c+d = 18.0 in
Perimeter of Critical Section, b 0= 4 * b 1 = 72.0 in
Nominal Shear Strength provided by Concrete (According to Eq. 11-33 of ACI318), V c=
* •4 * f' c * b 0 * / d 1000
• = 109.3 kips
Punching Shear Reinforcement is : IF(V u> •• V c;" Required";"Not Required") = Required
Interactive Design Aids for Structural Engineers
Chapter 1: Concrete Design ACI 318
Punching Shear Reinforcement on Slab Page: 40
Determine Area of Shear Reinforcement
Minimum Effective Depth of Slab with Shear Reinforcement (According to Cl.11.11.3 of ACI318), d min=
MIN(6;16*Dia ) = 6.0 in
Effective Depth of Slab : IF(d>d min;" Should Increase";"OK") = OK
Maximum Shear Strength of Slab with Shear Reinforcement (According to Cl.11.11.3.2 of ACI318), V n=
* 6 • f' c * b 0 d* 1000
/ = 163.9 kips
Validity : IF(V u> •• V n;" Not Valid";"Valid") = Valid
Shear Strength provided by Concrete with Shear RFT (According to Cl.11.11.3.1 of ACI318), V ci=
* •2 * f' c * b 0 * / d 1000
• = 54.6 kips
Nominal Shear Strength provided by Reinforcement (According to Eq. 11-2 of ACI318),
V u - • * V ci
V s= = 105.4 kips
•
Spacing of Provided Bars, s= 3.0 in
Vs * * s 1000
Required Area of Reinforcement, A v= = 0.88 in 2
*fyd
Required Area of Reinforcement for each side of Column, A v_side= /Av4 = 0.22 in 2
Perimeter of Critical Section where Shear Reinforcement may be terminated,
V u 1000
*
b' 0= = 210.8 in
• * * •2 *
• f' c d*
Distance from Column Face where Shear Reinforcement may be terminated,
b' 0
a=
• 4 c -• 2 •/ = 28.8 in
Design Summary
Required Area of Reinforcement, A v= A v = 0.88 in 2
Distance from Column Face where Shear Reinforcement may be terminated: a = 28.8 in
Interactive Design Aids for Structural Engineers
Chapter 1: Concrete Design ACI 318
One Way Joist Page: 41
Design of One Way Joist as per ACI 318-11 Chapters 9 & 11
One Way Joist
Lne Lni
ts b
Lne Lni
System
Width of Beam, b= 30.0 in
Width of Joist, b j= 6.0 in
Spacing between Joists, s= 36.0 in
Slab Thickness, t s= 3.5 in
Exterior Joist Span, L ne= 27.5 ft
Interior Joist Span, L ni= 27.0 ft
Concrete Cover, co= 1.25 in
Load
Dead Load, DL= 130 psf
Live Load, LL= 60 psf
1.2 * DL + 1.6 LL
* s
Ultimate Load, w u= * = 0.756 kip/ft
1000 12
Interactive Design Aids for Structural Engineers
Chapter 1: Concrete Design ACI 318
One Way Joist Page: 42
Material Properties
Concrete Strength, f' c= 4000 psi
Yield Strength of Reinforcement, f y= 60000 psi
Tension Strength Reduction Factor (According to Cl.9.3.2 of ACI318), •= 0.90
Modification Factor for Lightweight Concrete, •• • 1.00
Factor for Rectangular Compressive Stress Block (According to Cl.10.2.7.3),
• 1=
IF(f' c • 4000;0.85;IF(f' c • 8000;0.65;1.05-0.00005*f' c)) = 0.85
Moment Distribution for Joist
1. End Span
2
w u L* ne
Edge Negative Moment for Exterior Joist, M nee= = 23.8 kip*ft
24
2
w u L* ne
Positive Moment for Exterior Joist, M pe= = 40.8 kip*ft
14
w u •* • L ne L +ni • / 2 2•
Negative Moment for Exterior Joist, M ne= = 56.1 kip*ft
10
2. Interior Spans
2
w u L* ni
Negative Moment for Interior Joist, M ni= = 50.1 kip*ft
11
2
w u L* ni
Positive Moment for Interior Joist , M pi= = 34.4 kip*ft
16
3. Maximum Moment M max=
MAX(M nee; M pe; M ne; M ni; M pi) = 56.1 kip*ft
Interactive Design Aids for Structural Engineers
Chapter 1: Concrete Design ACI 318
One Way Joist Page: 43
Calculation of Required Depth for Joist
• t=
0.319 * f' c * • 1 / f y = 0.01808
For Reasonable Deflection Control, choose a Reinforcement Ratio ( •)• equal to about one-half ( • t) •
Reinforcement Ratio, •= • t/ 2 = 0.00904
fy
• = • * = 0.13560
f' c
M max 12000
*
Required Depth, d=
• • * bj * f'c *• *•1 - 0.59 • * •
= 15.8 in
Required Thickness, h req= d + co = 17.1 in
h min= MAX(L ne* 12+b; L ni* 12+b;)/18.5 = 19.5 in
Provided Thickness, h= MAX(h req; h min) = 19.5 in
Effective Depth of Joist, d j= h-co = 18.25 in
Calculation of Required Reinforcement for Exterior Negative Moment of End Span (A sc1)
M nee 12000
*
R n1= = 159 psi
2
• * *bjdj
Reinforcement Ratio, • •= 0.85 f' *c
fy •
* -1 ••
1 * 2 R n1
0.85 f' *c
• = 0.0027
Area of Reinforcement, A s1= • •
*bj*dj = 0.30 in 2
Minimum Area of Reinforcement (According to Cl.10.5 of ACI318),
* 3 • f' c * *bjdj
A s_min1= = 0.35 in 2
fy
200 * *bjdj
A s_min2= = 0.36 in 2
fy
A s_min= MAX(A s_min1 ; A s_min2) = 0.36 in 2
Required Area of Reinforcement, A sc1= MAX(A s1; A s_min) = 0.36 in 2
Provided Reinforcement, Bar= SEL("ACI/Bar"; Bar; ) = No.3
Provided Reinforcement, A sb= TAB("ACI/Bar"; Asb; Bar=Bar) = 0.11 in 2
Number of Bars, n= 4
Vertical Reinforcement, A sc1_Prov= A sb * n = 0.44 in 2
Check Validity= IF(A sc1_Prov • A sc1; " Valid"; "Invalid") = Valid
Interactive Design Aids for Structural Engineers
Chapter 1: Concrete Design ACI 318
One Way Joist Page: 44
Calculation of Required Reinforcement for Positive Moment of End Span (A sc2)
M pe 12000
*
R n2= = 272 psi
2
• * *bjdj
Reinforcement Ratio, • •= 0.85 f' *c
fy •* -1 ••
1 * 2 R n2
0.85 f' *c
• = 0.0047
Area of Reinforcement, A s2= • •
*bj*dj = 0.51 in 2
Minimum Area of Reinforcement (According to Cl.10.5 of ACI318),
* 3 • f' c * *bjdj
A s_min1= = 0.35 in 2
fy
200 * *bjdj
A s_min2= = 0.36 in 2
fy
A s_min= MAX(A s_min1 ; A s_min2) = 0.36 in 2
Required Area of Reinforcement, A sc2= MAX(A s2; A s_min) = 0.51 in 2
Provided Reinforcement, Bar= SEL("ACI/Bar"; Bar; ) = No.5
Provided Reinforcement, A sb= TAB("ACI/Bar"; Asb; Bar=Bar) = 0.31 in 2
Number of Bars, n= 2
Vertical Reinforcement, A sc2_Prov= A sb * n = 0.62 in 2
Check Validity= IF(A sc2_Prov • A sc2; " Valid"; "Invalid") = Valid
Calculation of Required Reinforcement for Interior Negative Moment of End Span (A sc3)
M ne 12000
*
R n3= = 374 psi
2
• * *bjdj
Reinforcement Ratio, • •= 0.85 f' *c
fy •* -1 ••
1 * 2 R n3
0.85 f' *c
• = 0.0066
Area of Reinforcement, A s3= • •
*bj*dj = 0.72 in 2
Minimum Area of Reinforcement (According to Cl.10.5 of ACI318),
* 3 • f' c * *bjdj
A s_min1= = 0.35 in 2
fy
200 * *bjdj
A s_min2= = 0.36 in 2
fy
A s_min= MAX(A s_min1 ; A s_min2) = 0.36 in 2
Required Area of Reinforcement, A sc3= MAX(A s3; A s_min) = 0.72 in 2
Interactive Design Aids for Structural Engineers
Chapter 1: Concrete Design ACI 318
One Way Joist Page: 45
Provided Reinforcement, Bar= SEL("ACI/Bar"; Bar; ) = No.5
Provided Reinforcement, A sb= TAB("ACI/Bar"; Asb; Bar=Bar) = 0.31 in 2
Number of Bars, n= 3
Vertical Reinforcement, A sc3_Prov= A sb * n = 0.93 in 2
Check Validity= IF(A sc3_Prov • A sc3; " Valid"; "Invalid") = Valid
Calculation of Required Reinforcement for Interior Negative Moment of Interior Span (A sc4)
M ni 12000
*
R n4= = 334 psi
2
• * *bjdj
Reinforcement Ratio, • •= 0.85 f' *c
fy •* -1 ••
1 * 2 R n4
0.85 f' *c
• = 0.0059
Area of Reinforcement, A s4= • •
*bj*dj = 0.65 in 2
Minimum Area of Reinforcement (According to Cl.10.5 of ACI318),
* 3 • f' c * *bjdj
A s_min1= = 0.35 in 2
fy
200 * *bjdj
A s_min2= = 0.36 in 2
fy
A s_min= MAX(A s_min1 ; A s_min2) = 0.36 in 2
Required Area of Reinforcement, A sc4= MAX(A s4; A s_min) = 0.65 in 2
Provided Reinforcement, Bar= SEL("ACI/Bar"; Bar; ) = No.5
Provided Reinforcement, A sb= TAB("ACI/Bar"; Asb; Bar=Bar) = 0.31 in 2
Number of Bars, n= 3
Vertical Reinforcement, A sc4_Prov= A sb * n = 0.93 in 2
Check Validity= IF(A sc4_Prov • A sc4; " Valid"; "Invalid") = Valid
Interactive Design Aids for Structural Engineers
Chapter 1: Concrete Design ACI 318
One Way Joist Page: 46
Calculation of Required Reinforcement for Interior Positive Moment of Interior Span (A sc5)
M pi 12000
*
R n5= = 230 psi
2
• * *bjdj
Reinforcement Ratio, • •= 0.85 f' *c
fy •* -1 ••
1 * 2 R n5
0.85 f' *c
• = 0.0040
Area of Reinforcement, A s5= • •
*bj*dj = 0.44 in 2
Minimum Area of Reinforcement (According to Cl.10.5 of ACI318),
* 3 • f' c * *bjdj
A s_min1= = 0.35 in 2
fy
200 * *bjdj
A s_min2= = 0.36 in 2
fy
A s_min= MAX(A s_min1 ; A s_min2) = 0.36 in 2
Required Area of Reinforcement, A sc5= MAX(A s5; A s_min) = 0.44 in 2
Provided Reinforcement, Bar= SEL("ACI/Bar"; Bar; ) = No.5
Provided Reinforcement, A sb= TAB("ACI/Bar"; Asb; Bar=Bar) = 0.31 in 2
Number of Bars, n= 2
Vertical Reinforcement, A sc5_Prov= A sb * n = 0.62 in 2
Check Validity= IF(A sc5_Prov • A sc5; " Valid"; "Invalid") = Valid
Design Summary
Area of Reinforcement for Exterior Negative Moment of End Span: A sc1_Prov = 0.44 in 2
Area of Reinforcement for Positive Moment of End Span: A sc2_Prov = 0.62 in 2
Area of Reinforcement for Interior Negative Moment of End Span: A sc3_Prov = 0.93 in 2
Area of Reinforcement for Interior Negative Moment of Interior Span: A sc4_Prov = 0.93 in 2
Area of Reinforcement for Interior Positive Moment of Interior Span: A sc5_Prov = 0.62 in 2
Interactive Design Aids for Structural Engineers
Chapter 1: Concrete Design ACI 318
Two-Way Slab Analyzed by the Direct Design Method Page: 47
Design Two-Way Slab without Beams Analyzed by the Direct Design Method As per ACI 318-11
Two-Way Slab Analyzed by the Direct Design Method
Design
Strip
Ln
Ln
Ln
Ls Ls Ls
System
Longer Span for Two-Way Slab, L n= 18.00 ft
Shorter Span for Two-Way Slab, L s= 14.00 ft
Thickness of Slab, h= 7.00 in
Concrete Cover, co= 1.25 in
Depth of Slab, d= h-co = 5.75 in
Square Column Dimension, b c= 16.00 in
Width of Column Strip, b= Ls*12 / 2 = 84 in
Width of Middle Strip, b m= Ls*12 - b = 84 in
Load
Slab Self Weight, q s= h/12 * 150 = 87.50 psf
Partition Load, q p= 20.00 psf
Dead Load, q D= qs+qp = 107.50 psf
Live Load, q L= 40.00 psf
Ultimate Load, q U= 1.2 * q D + 1.6 * q L = 193.00 psf
Material Properties
Concrete Strength, f' c= 3000 psi
Yield Strength of Reinforcement, f y= 60000 psi
Interactive Design Aids for Structural Engineers
Chapter 1: Concrete Design ACI 318
Two-Way Slab Analyzed by the Direct Design Method Page: 48
Tension Strength Reduction Factor (According to Cl.9.3.2 of ACI318), •= 0.90
Minimum Reinforcement Ratio (According to Cl.7.12.2 of ACI318),
• min=
IF(f y • 50000;0.002;IF(f y • 77143;0.0014;0.0018)) = 0.0018
Total Static Moment of Slab
Total Factored Static Moment Per Span (According to Eq. 13-4 of ACI318),
2
q U L* s bc
M 0=
* 8 1000 •
* Ln -
12
• = 93.82 kip*ft
Flexural Reinforcement Required for Negative Moment of Column Strip
M 0 12000
* 0.53*
R n1= = 239 psi
• * *bd2
• ••
0.85 f' *c * 2 R n1
Ratio of RFT, • •=
fy
* -1 1
0.85 f' *c
• = 0.00419
Area of Steel, A s1_Req= MAX( • 1; • min) * b * d = 2.02 in²
Provided Reinforcement, Bar= SEL("ACI/Bar"; Bar; ) = No.6
Provided Reinforcement, A sb= TAB("ACI/Bar"; Asb; Bar=Bar) = 0.44 in 2
Number of Bars, n= 5
Vertical Reinforcement, A s1_Prov= A sb * n = 2.20 in 2
Check Validity= IF(A s1_Prov • A s1_Req; " Valid"; "Invalid") = Valid
Flexural Reinforcement Required for Positive Moment of Column Strip
M 0 12000
* 0.31*
R n2= = 140 psi
• * *bd2
• ••
0.85 f' *c * 2 R n2
Ratio of RFT, • •=
fy
* -1 1
0.85 f' *c
• = 0.00240
Area of Steel, A s2_Req= MAX( • 2; • min) * b * d = 1.16 in²
Provided Reinforcement, Bar= SEL("ACI/Bar"; Bar; ) = No.6
Provided Reinforcement, A sb= TAB("ACI/Bar"; Asb; Bar=Bar) = 0.44 in 2
Number of Bars, n= 3
Vertical Reinforcement, A s2_Prov= A sb * n = 1.32 in 2
Check Validity= IF(A s2_Prov • A s2_Req; " Valid"; "Invalid") = Valid
Interactive Design Aids for Structural Engineers
Chapter 1: Concrete Design ACI 318
Two-Way Slab Analyzed by the Direct Design Method Page: 49
Flexural Reinforcement Required for Negative Moment of Middle Strip
M 0 12000
* 0.17*
R n3= = 77 psi
• * *bd2
• ••
0.85 f'c* fy * 2 R n3
Ratio of RFT, • •= * -1 1
0.85 f'c*
• = 0.00130
Area of Steel, A s3_Req= MAX( • 3; • min) * b * d = 0.87 in²
Provided Reinforcement, Bar= SEL("ACI/Bar"; Bar; ) = No.6
Provided Reinforcement, A sb= TAB("ACI/Bar"; Asb; Bar=Bar) = 0.44 in 2
Number of Bars, n= 2
Vertical Reinforcement, A s3_Prov= A sb * n = 0.88 in 2
Check Validity= IF(A s3_Prov • A s3_Req; " Valid"; "Invalid") = Valid
Flexural Reinforcement Required for Positive Moment of Middle Strip
M 0 12000
* 0.21*
R n4= = 95 psi
• * *bd2
• ••
0.85 f'c* fy * 2 R n4
Ratio of RFT, • •= * -1 1
0.85 f'c*
• = 0.00161
Area of Steel, A s4_Req= MAX( • 4; • min) * b * d = 0.87 in²
Provided Reinforcement, Bar= SEL("ACI/Bar"; Bar; ) = No.6
Provided Reinforcement, A sb= TAB("ACI/Bar"; Asb; Bar=Bar) = 0.44 in 2
Number of Bars, n= 2
Vertical Reinforcement, A s4_Prov= A sb * n = 0.88 in 2
Check Validity= IF(A s4_Prov • A s4_Req; " Valid"; "Invalid") = Valid
Design Summary
Area of Reinforcement Required for Negative Moment of Middle Strip,
A s1_Prov= A s1_Prov = 2.20 in 2
Area of Reinforcement Required for Negative Moment of Middle Strip,
A s2_Prov= A s2_Prov = 1.32 in 2
Area of Reinforcement Required for Negative Moment of Middle Strip,
A s3_Prov= A s3_Prov = 0.88 in 2
Area of Reinforcement Required for Positive Moment of Middle Strip,
A s4_Prov= A s4_Prov = 0.88 in 2
Interactive Design Aids for Structural Engineers
Chapter 1: Concrete Design ACI 318
Development Length of Bars in Tension Page: 50
Calculating Development Length of Bars in Tension as per ACI 318-11 Chapter 12
Development Length of Bars in Tension Lab Splice
Lab Splice
Material Properties
Concrete Strength, f' c= 4000 psi
Yield Strength of Reinforcement, f y= 60000 psi
Modification Factor for Lightweight Concrete, •• • 0.75
Factor of Development Length Based on RFT Location (According to Cl.12.2.4 of ACI318),
• t=
1.30
Factor of Development Length Based on RFT Coating (According to Cl.12.2.4 of ACI318),
• e=
1.50
Maximum Modifying Factor, • te= MIN( • t* • e; 1.7) = 1.70
Identification of, Bar= SEL("ACI/Bar" ;Bar; ) = No.7
Diameter of Bars, d b= TAB("ACI/Bar" ;Dia ;Bar=Bar ) = 0.88 in
Calculation of Development Length
1. Class A Splice
Development Length for Bars No.6 and Smaller (According to Cl.12.2.2 of ACI318),
* 3 f *y • te
L d_A1=
• 50 •* • f'* c
• * db = 114 in
Development Length for Bars No.7 and Greater (According to Cl.12.2.2 of ACI318),
* 3 f *y • te
L d_A2=
• 40 •* • f'* c
• * db = 142 in
L d_A= IF(d b • 0.75 ; L d_A1 ; L d_A2 ) = 142 in
2. Class B Splice
Development Length for Bars No.6 and Smaller (According to Cl.12.2.2 of ACI 318),
* 3 f *y • te
L d_B1=
• 50 •* • f'* c
• * 1.3 d* b = 148 in
Interactive Design Aids for Structural Engineers
Chapter 1: Concrete Design ACI 318
Development Length of Bars in Tension Page: 51
Development Length for Bars No.7 and Greater (According to Cl.12.2.2 of ACI318),
* 3 f *y • te
L d_B2=
• 40 •* • f'* c
• * 1.3 d* b = 184 in
L d_B= IF(d b • 0.75 ; L d_B1 ; L d_B2 ) = 184 in
Calculation Summary
Development Length for Class A, L d_A= L d_A = 142 in
Development Length for Class B, L d_B= L d_B = 184 in
Interactive Design Aids for Structural Engineers
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- TS1042 Sambungan Baut 01 Ganjil 2015 PDFDokumen20 halamanTS1042 Sambungan Baut 01 Ganjil 2015 PDFVicky RamadiBelum ada peringkat
- 4 SBB DET3107 Flexure 2 DesainDokumen23 halaman4 SBB DET3107 Flexure 2 DesainDwi GintingBelum ada peringkat
- Sistem Sambungan Pada Bangunan Baja2Dokumen35 halamanSistem Sambungan Pada Bangunan Baja2Junaid Arrasyid Muhammad100% (2)
- 7962 IdDokumen20 halaman7962 IdesterBelum ada peringkat
- 05 Balok LenturDokumen48 halaman05 Balok LenturShendy Arnaldo ValentinoBelum ada peringkat
- 04 Long TermDokumen25 halaman04 Long TermNovi Andry100% (1)
- Kuliah 2 Analisis Kekuatan Balok Untuk LenturDokumen111 halamanKuliah 2 Analisis Kekuatan Balok Untuk LenturEster SianiparBelum ada peringkat
- Macam Macam Sambungan BajaDokumen22 halamanMacam Macam Sambungan Bajafiona100% (1)
- 3915 8401 1 SMDokumen8 halaman3915 8401 1 SMWawan DevBelum ada peringkat
- 2a Andre Rangga Nugraha 120130039 Tugas 2 Rek - GempaDokumen6 halaman2a Andre Rangga Nugraha 120130039 Tugas 2 Rek - GempaAndre RanggaBelum ada peringkat
- Metode Konstruksi Offshore Platform - 2017!4!4Dokumen108 halamanMetode Konstruksi Offshore Platform - 2017!4!4asyhanggraini100% (4)
- AFA Conecting RodDokumen54 halamanAFA Conecting RodmatieladelBelum ada peringkat
- Materi PelatihanDokumen123 halamanMateri PelatihanAndi Setiawan100% (2)
- Seminar ProposalDokumen19 halamanSeminar ProposalAni HardianiBelum ada peringkat
- Jembatan Rangka BajaDokumen84 halamanJembatan Rangka BajaBoncuBelum ada peringkat
- Rangkuman SNI 7973-2017Dokumen17 halamanRangkuman SNI 7973-2017Trifena TutuBelum ada peringkat
- Tekan-Lentur Kayu PDFDokumen7 halamanTekan-Lentur Kayu PDFYuliar Azmi AdhitamaBelum ada peringkat
- Pertemuan 1 Konstruksi Baja 3 Sambungan Baut 09022022Dokumen55 halamanPertemuan 1 Konstruksi Baja 3 Sambungan Baut 09022022Shahia RafaBelum ada peringkat
- 00 LongtermDokumen26 halaman00 LongtermHafizh MufadhalBelum ada peringkat
- Perubahan Dari SNI 1729 2015 Ke 1729 2020Dokumen61 halamanPerubahan Dari SNI 1729 2015 Ke 1729 2020Agus DermawanBelum ada peringkat
- Pengaruh Main HoopDokumen15 halamanPengaruh Main HoopRudy ArthaBelum ada peringkat
- Sambungan Baut Awal 2Dokumen47 halamanSambungan Baut Awal 2yemima RanaBelum ada peringkat
- Analisis Desain Kolom Pendek Terhadap Beban KonsentrikDokumen13 halamanAnalisis Desain Kolom Pendek Terhadap Beban KonsentrikclvndinoBelum ada peringkat
- Perhitungan Baja HoneycombDokumen43 halamanPerhitungan Baja Honeycombdeanz_7589% (9)
- Pengencangan BautDokumen36 halamanPengencangan Bautmunajat tiliBelum ada peringkat
- Pendahuluan Struktur Beton LanjutDokumen5 halamanPendahuluan Struktur Beton LanjutGilang Pandu WinataBelum ada peringkat
- Arfa'i Abdi Elyan - Tugas Terstruktur 5 SoalDokumen24 halamanArfa'i Abdi Elyan - Tugas Terstruktur 5 SoalArfa'i Abdi ElyanBelum ada peringkat
- TS1042 Batang Tarik Ganjil 2015 (Pert.3)Dokumen21 halamanTS1042 Batang Tarik Ganjil 2015 (Pert.3)David MarshalBelum ada peringkat
- BalokDokumen11 halamanBalokAhmad BaehaqiBelum ada peringkat
- Perencanaan Kolom PendekDokumen26 halamanPerencanaan Kolom PendekaryayyyBelum ada peringkat
- Jawaban Atas Pertanyaan Pada Pelatihan CIBE ITB (STRUKTUR) 2019 + FlowchartDokumen5 halamanJawaban Atas Pertanyaan Pada Pelatihan CIBE ITB (STRUKTUR) 2019 + FlowchartMadhaneBelum ada peringkat
- Sistem Struktur Rangka KakuDokumen29 halamanSistem Struktur Rangka KakuindraBelum ada peringkat
- 3053 9205 1 PBDokumen4 halaman3053 9205 1 PBANISAH KHUSNUL KHOTIMAHBelum ada peringkat
- FormatDokumen61 halamanFormatErwin Tallu SangrapuBelum ada peringkat
- Material Dan Proses Produksi RivetDokumen14 halamanMaterial Dan Proses Produksi RivetRefky FBelum ada peringkat
- Sistem Struktur R & FDokumen9 halamanSistem Struktur R & FWillzAgahariBelum ada peringkat
- Sistem Rangka KakuDokumen31 halamanSistem Rangka KakuAnthonio ZogenBelum ada peringkat
- Mbs Boxing DecentrasiDokumen9 halamanMbs Boxing DecentrasiHery Poernomo100% (1)
- PresentationDokumen29 halamanPresentationHananto imawanBelum ada peringkat
- Fungsional Cusp BevelDokumen8 halamanFungsional Cusp BevelBilly Anderson SinagaBelum ada peringkat
- Bantalan GelindingDokumen11 halamanBantalan GelindingDede PermanaBelum ada peringkat
- Struktur Batang (Ikhwan Andre H - 201745500173)Dokumen10 halamanStruktur Batang (Ikhwan Andre H - 201745500173)Muhammad Ikhwan NasutionBelum ada peringkat
- Modul 3Dokumen8 halamanModul 3Purnama Sakhrial PradiniBelum ada peringkat
- Sambungan Elemen MesinDokumen69 halamanSambungan Elemen MesinNovita Sari100% (1)
- Pertemuan 11 - Perencanaan Sambungan Las - 17-6-2022-DikompresiDokumen25 halamanPertemuan 11 - Perencanaan Sambungan Las - 17-6-2022-DikompresiBara PrakosaBelum ada peringkat
- 8778 28205 1 PBDokumen12 halaman8778 28205 1 PBAlfiananda RahmadiskaBelum ada peringkat
- Materi Struktur Baja - 2Dokumen32 halamanMateri Struktur Baja - 2Reske SufitriBelum ada peringkat
- 201608-CPD Ahli Pracetak Prategang-15-01-Teknologi Aplikasi Beton Pracetak Prategang Bidang Perumahan PermukimanDokumen69 halaman201608-CPD Ahli Pracetak Prategang-15-01-Teknologi Aplikasi Beton Pracetak Prategang Bidang Perumahan PermukimanLiant PutraBelum ada peringkat
- RodaDokumen48 halamanRodaRuhari S.TBelum ada peringkat
- Tugas Review Tentang Desain Sambungan Mur Baut Dan PorosDokumen9 halamanTugas Review Tentang Desain Sambungan Mur Baut Dan PorosSyafei MuhamaadBelum ada peringkat
- Kelompok 3 Sistem Rangka Bresing Eksentrik (Srbe) VDokumen24 halamanKelompok 3 Sistem Rangka Bresing Eksentrik (Srbe) VrizalBelum ada peringkat
- Sambungan LASDokumen22 halamanSambungan LASOchnata Charis YuliantoBelum ada peringkat
- Perencanaan Struktur Baja DaktailDokumen38 halamanPerencanaan Struktur Baja DaktailRiko Riswandha Fahmi Prasetyo50% (2)
- Proposal Satria Bagaskoro 5211420041 FixDokumen21 halamanProposal Satria Bagaskoro 5211420041 FixWhoAmI ?Belum ada peringkat
- Desain Rigid Pavement Menggunakan Macro Excel, Tony Hartono BagioDokumen15 halamanDesain Rigid Pavement Menggunakan Macro Excel, Tony Hartono BagioTony Wang100% (1)
- RSAX2022 (Release 2.0) (Aplikasi Response Spektra Dengan Macro Excel)Dokumen5 halamanRSAX2022 (Release 2.0) (Aplikasi Response Spektra Dengan Macro Excel)Tony WangBelum ada peringkat
- VCmaster US Catalog 01concrete01-28 IdDokumen28 halamanVCmaster US Catalog 01concrete01-28 IdTony WangBelum ada peringkat
- AHPDS, Analisa Hidrologi Dan Perencanaan Dimensi Saluran, Oleh Tony Hartono BagioDokumen21 halamanAHPDS, Analisa Hidrologi Dan Perencanaan Dimensi Saluran, Oleh Tony Hartono BagioTony WangBelum ada peringkat
- ANAKOMP (Perkerasan Lentur Flexible Pavement), Tony Hartono BagioDokumen41 halamanANAKOMP (Perkerasan Lentur Flexible Pavement), Tony Hartono BagioTony WangBelum ada peringkat
- Dinamika Struktur Tony Hartono BagioDokumen15 halamanDinamika Struktur Tony Hartono BagioTony WangBelum ada peringkat
- Dinamika StrukturDokumen4 halamanDinamika StrukturTony WangBelum ada peringkat
- AHPDS (Analisis Hidrologi Dan Perencanaan Dimensi Saluran)Dokumen21 halamanAHPDS (Analisis Hidrologi Dan Perencanaan Dimensi Saluran)Tony WangBelum ada peringkat
- 05 Persamaan RegresiDokumen2 halaman05 Persamaan RegresiTony WangBelum ada peringkat
- 01KolomAxial 2017-03-07 ContohSoalDokumen6 halaman01KolomAxial 2017-03-07 ContohSoalTony WangBelum ada peringkat
- Koefisien Analisa Harga Satuan SNI: 2008Dokumen82 halamanKoefisien Analisa Harga Satuan SNI: 2008Tony WangBelum ada peringkat
- BAB02AnalisaBalokLentur PDFDokumen14 halamanBAB02AnalisaBalokLentur PDFTony WangBelum ada peringkat
- 01KolomAxial 2017-03-07 ContohSoalDokumen4 halaman01KolomAxial 2017-03-07 ContohSoalTony WangBelum ada peringkat
- Perhitungan KolomDokumen14 halamanPerhitungan KolomMuh Zulkarnain83% (6)
- Beton2 10 MBC KolomBergoyangDokumen15 halamanBeton2 10 MBC KolomBergoyangTony WangBelum ada peringkat