100% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (1 suara)
337 tayangan41 halamanPanduan Lengkap KPI dan OKR
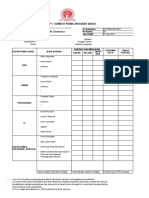
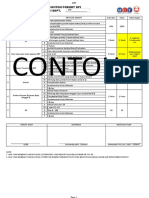
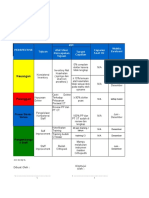
Dokumen tersebut membahas tentang pengertian, kepentingan, dan cara membuat Key Performance Indicator (KPI). KPI merupakan ukuran kinerja penting yang fokus pada aspek kritis bagi kesuksesan organisasi. KPI membantu komunikasi strategi dan mengukur kinerja secara obyektif. Ada beberapa tingkatan dalam membuat KPI mulai dari absensi, shared KPI, job description, hingga balanced scorecard dan continuous performance.
Diunggah oleh
Alexius Julio BrianHak Cipta
© © All Rights Reserved
Kami menangani hak cipta konten dengan serius. Jika Anda merasa konten ini milik Anda, ajukan klaim di sini.
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PDF, TXT atau baca online di Scribd
100% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (1 suara)
337 tayangan41 halamanPanduan Lengkap KPI dan OKR
Dokumen tersebut membahas tentang pengertian, kepentingan, dan cara membuat Key Performance Indicator (KPI). KPI merupakan ukuran kinerja penting yang fokus pada aspek kritis bagi kesuksesan organisasi. KPI membantu komunikasi strategi dan mengukur kinerja secara obyektif. Ada beberapa tingkatan dalam membuat KPI mulai dari absensi, shared KPI, job description, hingga balanced scorecard dan continuous performance.
Diunggah oleh
Alexius Julio BrianHak Cipta
© © All Rights Reserved
Kami menangani hak cipta konten dengan serius. Jika Anda merasa konten ini milik Anda, ajukan klaim di sini.
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PDF, TXT atau baca online di Scribd