IKP PATOLOGI Ke-4 InfHealHemopoetik256
Diunggah oleh
yudhaHak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
IKP PATOLOGI Ke-4 InfHealHemopoetik256
Diunggah oleh
yudhaHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
PATOLOGI ANATOMI &
PATOLOGI KLINIK
Radang, Pemulihan
Jaringan & Sistem
Hemopoetik
Oleh:
Yudha Anggit J, S.Kep, M.Kes
“Wahai Tuhanku, tambahkanlah pengetahuan
kepadaku dan anugerahkanlah pemahaman
kepadaku…amin”
Radang (Inflamasi)
Definisi= Respon dari jaringan hidup terhadap
cedera, yang menimbulkan eksudat (cairan kaya
protein (kecuali eksudat bening/serous) yg
keluar dari vaskuler).
Manifestasi= - Lokal
- Umum
* transudat= cairan keluar melalui suatu membran baik
dari vaskuler maupun jaringan, cenderung sangat cair
dan kurang bahan padatnya.
Manifestasi Lokal:
1. Makroskopik: panas (kalor), nyeri (dolor), bengkak
(tumor), kemerahan (rubor) & berkurangnya fungsi
(functio laesa)
5 “tanda radang yg utama” dirintis oleh Celsus.
2. Mikroskopik: konstriksi arteriolar sementara -
vasodilatasi - permeabilitas dinding vaskuler -
eksudat - hemokonsentrasi - marjinasi leukosit -
emigrasi leukosit & diapedesis eritrosit - kemotaksis
leukosit PMN - fagositosis - timbul makrofag /
histiosit fagositik
Extravasation of leukocyte
Margination, rolling, adhesion, diapedesis, chemotaxis
& phagocyitosis
3. Komponen dasar 1) Vaskular
Manifestasi Lokal : 2) Selular
3) Eksudat
Vaskular: Terjadi peningkatan aliran darah yg
relatif statik pada daerah radang rubor &
kalor
Selular
Dari darah: - Leukosit PMN (Polimorfonuklear)
- Limfosit (T & B) imun selular &
humoral
- Monosit
Dari jaringan: - Histiosit / Makrofag jaringan
- Fibroblas
- Sel datia
* Leukosit PMN= Neutrofil (sel pertama & terbanyak pada
radang akut; 60% dari seluruh leukosit), Eosinofil (kebanyakan
berkaitan dgn infeksi parasit dan alergi; 3% dari leukosit) &
Basofil & sel mast (kebanyakan pada penyakit yg diperantarai
sistem imun; 1% dari leukosit)
* Limfosit (30% dari leukosit)= tidak mencapai daerah radang
pada stadium dini, tapi penting pada radang kronik
* Monosit (6% dari leukosit)= merupakan sel fagosit jumlahnya
sedikit, respon kemotaksis lemah
* Histiosit= morfologi mirip monosit, aktif dalam fagositosis
* Fibroblas= sel fibrosa muda pada stadium peyembuhan
* Sel datia= sel besar berinti banyak berupa fusi dari histiosit,
banyak macamnya namun yg sering adalah sel datia benda
asing (inti tersusun sentral) & sel datia Langhans (inti tersusun
perifer membentuk susunan "tapal kuda")
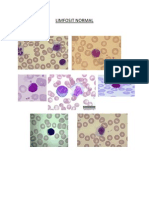
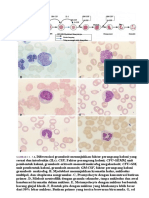
Silsilah Sel Darah
(Stem Cell Differentiation and Hematopoesis)
Jenis Radang dgn sel-sel khasnya:
1. Akut: Leukosit PMN, kecuali tifoid.
2. Subakut: Leukosit PMN, Sel plasma & Limfosit.
3. Kronik: Limfosit, Sel plasma & Fibroblas.
* Pada semua jenis radang ditemukan monosit
dan makrofag, walau bervariasi.
*Comparison between acute and chronic inflammation:
Acute Chronic
Persistent acute inflammation due to non-degradable
Causative
Pathogens, injured tissues pathogens, persistent foreign bodies, or autoimmune
agent
reactions
Major cells Mononuclear cells (monocytes, macrophages, lymphocytes,
Neutrophils
involved plasma cells), fibroblasts
Primary INF-γ and other cytokines, growth factors, reactive oxygen
Vasoactive amines, eicosanoids
mediators species, hydrolytic enzymes
Onset Immediate Delayed
Duration Few days Up to many months, or years
Healing, abscess formation,
Outcomes Tissue destruction, fibrosis
chronic inflammation
Eksudat: Karena 2 hal yaitu Dilatasi arteriolar &
Peningkatan permeabilitas vaskular
* Perantara kimiawi yg sering:
Amin (histamin aktif / hidroksitriptamin / serotonin
vasodilatasi & permeabilitas vaskular);
Kinin (bradikinin & kalidin vasodilatasi, permeabilitas
vaskular & nyeri);
Protease (dari neutrofil, beberapa merupakan pirogen
permeabilitas vaskular, pelepasan histamin, kemotaktik untuk
monosit, membelah C3 dan C5, mengaktivasi kinin & imobilisasi
neutrofil);
Derivat komplemen (misalnya C3a & C5a pelepasan
histamin dari sel mast, agen kemotaktik);
Prostaglandin (dilepas neutrofil dan trombosit, midal PGE1 dan
PGE2 vasodilatasi, demam & nyeri, mempotensial aksi kinin
& efek protektif);
Zat anafilaksi reaksi lambat (SRS-A) ( permeabilitas vaskular,
bronkospasme)
Plasma derived mediators
(Perantara kimiawi dari plasma)
Name Produced by Description
A vasoactive protein which is able to induce vasodilation, increase vascular
Bradykinin Kinin system
permeability, cause smooth muscle contraction, and induce pain.
Cleaves to produce C3a and C3b. C3a stimulates histamine release by mast
Complement cells, thereby producing vasodilation. C3b is able to bind to bacterial cell
C3
system walls and act as an opsonin, which marks the invader as a target for
phagocytosis.
Stimulates histamine release by mast cells, thereby producing vasodilation. It
Complement
C5a is also able to act as a chemoattractant to direct cells via chemotaxis to
system
the site of inflammation.
A protein which circulates inactively, until activated by collagen, platelets, or
exposed basement membranes via conformational change. When
Factor XII (Hageman
Liver activated, it in turn is able to activate three plasma systems involved in
Factor)
inflammation: the kinin system, fibrinolysis system, and coagulation
system.
A complex of the complement proteins C5b, C6, C7, C8, and multiple units of
Membrane attack Complement C9. The combination and activation of this range of complement proteins
complex system forms the membrane attack complex , which is able to insert into
bacterial cell walls and causes cell lysis with ensuing death.
Fibrinolysis Able to break down fibrin clots, cleave complement protein C3, and activate
Plasmin
system Factor XII.
Cleaves the soluble plasma protein fibrinogen to produce insoluble fibrin,
Coagulation which aggregates to form a blood clot. Thrombin can also bind to cells
Thrombin
system via the PAR1 receptor to trigger several other inflammatory responses,
such as production of chemokines and nitric oxide.
Cell derived mediators
Name Type Source Description
These cells contain a large variety of enzymes which perform a
number of functions. Granules can be classified as either
Lysosome specific or azurophilic depending upon the contents, and
Enzymes Granulocytes
granules are able to break down a number of substances, some of
which may be plasma-derived proteins which allow these
enzymes to act as inflammatory mediators.
Stored in preformed granules, histamine is released in response
Vasoactive
Histamine Mast cells, basophils, platelets to a number of stimuli. It causes arteriole dilation and
amine
increased venous permeability.
Antiviral, immunoregulatory, and anti-tumour properties. This
interferon was originally called macrophage-activating
IFN-γ Cytokine T-cells, NK cells
factor, and is especially important in the maintenance of
chronic inflammation.
Activation and chemoattraction of neutrophils, with a weak
IL-8 Chemokine Primarily macrophages
effect on monocytes and eosinophils.
Able to mediate leukocyte adhesion and activation, allowing
them to bind to the endothelium and migrate across it. In
Leukotriene
Eicosanoid Leukocytes neutrophils, it is also a potent chemoattractant, and is able
B4
to induce the formation of reactive oxygen species and the
release of lysosome enzymes by these cells.
Potent vasodilator, relaxes smooth muscle, reduces platelet
Macrophages, endothelial cells,
Nitric oxide Soluble gas aggregation, aids in leukocyte recruitment, direct
some neurons
antimicrobial activity in high concentrations.
A group of proteins which can cause vasodilation, fever, and
Prostaglandins Eicosanoid Mast cells
pain.
Both affect a wide variety of cells to induce inflammatory
reactions: fever, production of cytokines, endothelial gene
TNF-α and IL-
Cytokines Primarily macrophages regulation, chemotaxis, leukocyte adherence, activation of
1
fibroblasts. Responsible for the systemic effects of
inflammation, such as loss of appetite & heart rate.
Makroskopik lain dari Radang Akut:
- Serosa
- Fibrinosa
- Sero-fibrinosa
- Hemoragik
- Supuratif /purulen (: ulkus, abses, empiema)
- Kataral (sekresi mukoid yg banyak)
- Gangren (~trombosis, devitalisasi)
- Flegmon (~nekrosis edematosa)
- Membranosa
- Selulitis (~sedikit timbul, tepi merah, garis merah di
bawah kulit, nyeri tekan)
Manifestasi Umum:
- Demam
- Hiperpireksia
- Perubahan dalam darah (leukositosis,
leukopenia, anemia)
- Perubahan pada organ-organ (reaktif lokal
(:makrofag) & umum(:hiperplasi limfe),
degeneratif, septikemia, piemia & bakteriemia)
Perbaikan/Pemulihan Jaringan
(Wound Healing)
Sifat: Hasil akhir dicapai melalui 1) Regenerasi sel-
sel parenkim organ & 2) Petumbuhan jaringan ikat
penyokong
Mekanisme=
- Penyatuan primer
- Penyatuan sekunder (dgn granulasi)
- Perbaikan dgn resolusi
- Perbaikan dgn organisasi
- Perbaikan dgn regenerasi (~kecuali sistem saraf
gliosis & otot hipertrofi jaringan yg ada)
Faktor-faktor yg mempengaruhi Perbaikan:
- Jaringan yg terlibat
- Vaskularitas
- Proteksi
- Infeksi
- Gizi (~protein)
- Vitamin (vit. C untuk integritas dinding kapiler &
pematangan kolagen, pada scurvy (avit. C)
kemungkinan tidak ada penyembuhan sama sekali)
- Umur (~sirkulasi)
- Endokrin
- Suhu
- Ukuran cedera
- Benda asing debridement
- Sinus & fistula
- Iradiasi
- Saraf sensorik
Sistem Hemopoetik
Hemoglobin (normal laki dewasa= 13 – 188 g/dL;
wanita dewasa= 11,5 – 16,5 g/dL)
Suksinil Ko-A Glisin
Asam aminolevulinat (ALA) [2 buah]
Porfirin
Protoporfirin IX Besi
Globin Hem
Hemoglobin [4 buah]
Globin Hematin
Biliverdin Besi
Bilirubin
Bilirubin terkonjugasi
Urobilinogen, dst
Urobilin, dst
Beberapa nilai rujukan dewasa normal (satuan tradisional), plasma:
Besi= 60 - 190 μg/100ml
Bilirubin= total (0,3 - 1 mg/100ml); terkonjugasi (< 0,2
mg/100ml)
Folat= 5 - 20 ng/ml
Protein= total (6,2 - 8 g/100ml ); albumin (3,5 - 5,2
g/100ml)
Vit B12= 160 - 900 pg/ml
Vit C (asam askorbat)= > 0,3 mg/dL
Leukosit= 5 – 10 (x 109)/L
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Faktor ImplansiDokumen2 halamanFaktor ImplansindlaainiBelum ada peringkat
- Inflamasi 2Dokumen24 halamanInflamasi 2Enda Herawati SaragihBelum ada peringkat
- Imunologi InflamasiDokumen10 halamanImunologi InflamasieN AliminBelum ada peringkat
- InflamasiDokumen5 halamanInflamasiMikhael VersenBelum ada peringkat
- Mediator InflamasiDokumen3 halamanMediator InflamasiMa'Luvi Kholil100% (5)
- Sistem KomplemenDokumen46 halamanSistem KomplemenAstrid Damayanti100% (2)
- 4 Respon Imun Non SpesifikDokumen19 halaman4 Respon Imun Non SpesifiknadaBelum ada peringkat
- Inflamasi DR - Istiati Print2Dokumen42 halamanInflamasi DR - Istiati Print2HanifNurRasyidBelum ada peringkat
- Mediator InflamasiDokumen3 halamanMediator InflamasiTiara KusumaBelum ada peringkat
- Patologi, Inflamasi, InfeksiDokumen23 halamanPatologi, Inflamasi, Infeksifatihul matlubBelum ada peringkat
- Auliya Salsabila - 190501005 - Mekanisme InflamasiDokumen15 halamanAuliya Salsabila - 190501005 - Mekanisme InflamasiMANGSUP ARSYADIBelum ada peringkat
- InflamasiDokumen29 halamanInflamasirima tricesBelum ada peringkat
- Inflamasi Akut Dan KronisDokumen3 halamanInflamasi Akut Dan KronisCindy Noor PradiniBelum ada peringkat
- HEMATOPOEISISDokumen3 halamanHEMATOPOEISISUsan DaryamanBelum ada peringkat
- PERADANGAN (Inflamasi)Dokumen15 halamanPERADANGAN (Inflamasi)Eggi Yenniawati0% (1)
- Radang: Muhammad SowwamDokumen24 halamanRadang: Muhammad SowwamLia SariBelum ada peringkat
- (Idk 2) Respon Inflamasi Dan ResolusiDokumen16 halaman(Idk 2) Respon Inflamasi Dan ResolusiDiah KamiliyaBelum ada peringkat
- Hasil Akhir Inflamasi AkutDokumen7 halamanHasil Akhir Inflamasi AkutWinda S SigalinggingBelum ada peringkat
- 6.sistem Komplemen 1Dokumen19 halaman6.sistem Komplemen 1LarasBelum ada peringkat
- NEOPLASIADokumen6 halamanNEOPLASIAFajar Pra WicxBelum ada peringkat
- Imunopatogenesis GNADokumen17 halamanImunopatogenesis GNAAgung Gek SandraBelum ada peringkat
- B - 2 - Radang Dan Pemulihan JaringanDokumen26 halamanB - 2 - Radang Dan Pemulihan JaringanYudhy BasoBelum ada peringkat
- Mediator InflamasiDokumen3 halamanMediator InflamasiangieBelum ada peringkat
- Sistemkomplemen 140518052138 Phpapp02Dokumen21 halamanSistemkomplemen 140518052138 Phpapp02Mark Buloglabna - MoseBelum ada peringkat
- Proses PeradanganDokumen44 halamanProses PeradanganAraBelum ada peringkat
- Inflamasi Akut Dan KronikDokumen8 halamanInflamasi Akut Dan KronikGhaniRahmani100% (2)
- Radang, Degenerasi, NekrosisDokumen48 halamanRadang, Degenerasi, Nekrosismilton7777Belum ada peringkat
- TM 3 Imun Non Spesifik Dan Spesifik 6Dokumen94 halamanTM 3 Imun Non Spesifik Dan Spesifik 6Maria DewiBelum ada peringkat
- Respon Imun Non SpesifikDokumen15 halamanRespon Imun Non SpesifikMaulidia FebrianiBelum ada peringkat
- 3 Peradangan Dan Kerusakan Jaringan 22Dokumen26 halaman3 Peradangan Dan Kerusakan Jaringan 22Arie PhanyBelum ada peringkat
- INFLAMASIDokumen38 halamanINFLAMASIangrilahBelum ada peringkat
- B Proses InflamasiDokumen46 halamanB Proses Inflamasidiase3Belum ada peringkat
- 6.sistem KomplemenDokumen19 halaman6.sistem KomplemenBilqis NurganiyuBelum ada peringkat
- Kelompok 2 IDK2 (Resume Dan Vidio Praktek 3)Dokumen21 halamanKelompok 2 IDK2 (Resume Dan Vidio Praktek 3)AL KhodimanBelum ada peringkat
- Konsep Dasar PeradanganDokumen64 halamanKonsep Dasar PeradanganFaiseh100% (2)
- Cutaneous Vasculature and ImmuneDokumen31 halamanCutaneous Vasculature and ImmuneAri KurniawanBelum ada peringkat
- Radang & PerbaikanDokumen49 halamanRadang & PerbaikanKuntum KhoiraniBelum ada peringkat
- Imunologi DasarDokumen26 halamanImunologi DasarLidya AriastutiBelum ada peringkat
- Sistem Imun-KomplemenDokumen3 halamanSistem Imun-KomplemenrochmahBelum ada peringkat
- Sistem Imun Pada HewanDokumen44 halamanSistem Imun Pada HewanDhanyAl16Belum ada peringkat
- Limfosit NormalDokumen25 halamanLimfosit NormalsitichoriyahBelum ada peringkat
- Radang (Inflamasi)Dokumen32 halamanRadang (Inflamasi)ratihBelum ada peringkat
- Innate ImunDokumen6 halamanInnate ImunMalikhatul WafiyahBelum ada peringkat
- Clinical Laboratory Science-288-290Dokumen6 halamanClinical Laboratory Science-288-290Raven foxieBelum ada peringkat
- INFLAMASIDokumen34 halamanINFLAMASIIrene widya AribowoBelum ada peringkat
- SLEDokumen81 halamanSLEFitriani Nur RohmahBelum ada peringkat
- Mikrobiologi Perubatan I: Patogen dan Mikrobiologi ManusiaDari EverandMikrobiologi Perubatan I: Patogen dan Mikrobiologi ManusiaPenilaian: 2.5 dari 5 bintang2.5/5 (2)
- Mikrobiologi Medis I: Patogen dan Mikrobioma ManusiaDari EverandMikrobiologi Medis I: Patogen dan Mikrobioma ManusiaPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (11)
- PMK No. 26 TTG Tarif Pemeriksaan KesehatanDokumen27 halamanPMK No. 26 TTG Tarif Pemeriksaan KesehatanFitry HermawiratmajaBelum ada peringkat
- 7 Pendugaan ParameterDokumen48 halaman7 Pendugaan ParameteryudhaBelum ada peringkat
- 6 Distribusi SamplingDokumen24 halaman6 Distribusi SamplingyudhaBelum ada peringkat
- 5 Distribusi ProbabilitasDokumen51 halaman5 Distribusi ProbabilitasyudhaBelum ada peringkat
- 4 ProbabilitasDokumen38 halaman4 ProbabilitasyudhaBelum ada peringkat
- 8 Konsep Statistika Inferensial - LatihanDokumen15 halaman8 Konsep Statistika Inferensial - LatihanyudhaBelum ada peringkat
- Soal Kompetensi PATELKI Horison Mei 2012 Kamar 421Dokumen5 halamanSoal Kompetensi PATELKI Horison Mei 2012 Kamar 421HerlinaRizkiPrianitaBelum ada peringkat
- M3 Anatomi Buku PT 20 5 2014Dokumen20 halamanM3 Anatomi Buku PT 20 5 2014yudhaBelum ada peringkat
- Bukuajar Tahap6 Indeks InputDokumen7 halamanBukuajar Tahap6 Indeks InputyudhaBelum ada peringkat
- M2 Teknik&Strategi Menulis Buku 20 5 2014Dokumen40 halamanM2 Teknik&Strategi Menulis Buku 20 5 2014yudhaBelum ada peringkat
- M1 Ragam Buku PT 20 5 2014Dokumen11 halamanM1 Ragam Buku PT 20 5 2014yudhaBelum ada peringkat
- Tekanan Darah Dan Faktor Yang MempengaruhiDokumen25 halamanTekanan Darah Dan Faktor Yang MempengaruhiyudhaBelum ada peringkat
- Penulisan Buku Ajar - Menyisipkan Page BreakDokumen4 halamanPenulisan Buku Ajar - Menyisipkan Page BreakyudhaBelum ada peringkat
- Ukom Kimia Klinik D3 Poltekkes Kemenkes Mataram 2020Dokumen89 halamanUkom Kimia Klinik D3 Poltekkes Kemenkes Mataram 2020Indira PasyaBelum ada peringkat
- Konsep Pel Keluarga HarkitDokumen29 halamanKonsep Pel Keluarga HarkityudhaBelum ada peringkat
- Soal ToksikologiDokumen12 halamanSoal ToksikologiyudhaBelum ada peringkat
- KIMIA KLINIK Darmadi Buat YaaaaaaaaaDokumen3 halamanKIMIA KLINIK Darmadi Buat YaaaaaaaaayudhaBelum ada peringkat
- Diagnosa PXDokumen5 halamanDiagnosa PXyudhaBelum ada peringkat
- Trend Isu Kesehatan LansiaDokumen29 halamanTrend Isu Kesehatan LansiayudhaBelum ada peringkat
- Latihan Soal UkomDokumen26 halamanLatihan Soal UkomTri Harya80% (5)
- Keluarga VIDokumen35 halamanKeluarga VIRoad TovegasBelum ada peringkat
- Sistem Peredaran DarahDokumen23 halamanSistem Peredaran DarahyudhaBelum ada peringkat
- ANFIS PERNAFASAN 9 Sep 20Dokumen25 halamanANFIS PERNAFASAN 9 Sep 20yudhaBelum ada peringkat
- Soal Kompetensi Analis 2019Dokumen15 halamanSoal Kompetensi Analis 2019itaBelum ada peringkat
- Konsep Pel KeluargaDokumen42 halamanKonsep Pel KeluargayudhaBelum ada peringkat
- Aspek Legal FlebotomiDokumen12 halamanAspek Legal FlebotomiyudhaBelum ada peringkat
- Tekanan Darah Dan Faktor Yang MempengaruhiDokumen25 halamanTekanan Darah Dan Faktor Yang MempengaruhiyudhaBelum ada peringkat
- Komplikasi PlebotomiDokumen12 halamanKomplikasi PlebotomiyudhaBelum ada peringkat
- Darah Dan Pembuluh DarahDokumen41 halamanDarah Dan Pembuluh DarahFerryRajoBintangBelum ada peringkat
- AADKOMUNIKASIDokumen7 halamanAADKOMUNIKASIyudhaBelum ada peringkat