WPS
Diunggah oleh
Sohibul Hajah0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
66 tayangan25 halamanHak Cipta
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Format Tersedia
PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
66 tayangan25 halamanWPS
Diunggah oleh
Sohibul HajahHak Cipta:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Anda di halaman 1dari 25
1
WELDING CODE, STANDARD WELDING CODE, STANDARD
& WELDING PROCEDURE & WELDING PROCEDURE
Dr. Ir. Winarto, M.Sc.
DEPARTEMEN METALURGI & MATERIAL
FAKULTAS TEKNIK UNIVERISTAS INDONESIA
DEFINISI DEFINISI
nn Standard Standard adalah adalahkumpulan kumpulandokumen dokumen--dokumen dokumen berisikan berisikan
kode kode (codes), (codes), spesifikasi spesifikasi (specification), Saran (specification), Saran aplikasi aplikasi
(recommended practice), (recommended practice), klasifikasi klasifikasi, , dan dan petunjuk petunjuk (guide) (guide)
yang yang telah telahdipersiapkan dipersiapkanoleh oleh suatu suatu institusi institusi organisasi organisasi dan dan di di
sahkan sahkan (approved) (approved) sesuai sesuai dengan denganprosedur prosedur yang yang ada ada
((berlaku berlaku). ).
nn Codes Codes adalah adalahsuatu suatu standard yang standard yang berisikan berisikankondisi kondisi dan dan
persyaratan persyaratan yang yang berhubungan berhubungandengan denganbidang bidang khusus khusus (a (a
particularly subject) particularly subject) dan dan mengindikasikan mengindikasikanbahwa bahwa prosedur prosedur
yg yg digunakan digunakantelah telahsesuai sesuai dengan denganpersyaratannya persyaratannya. Codes . Codes ini ini
HARUS HARUS diikuti diikuti (mandatory) (mandatory) karena karena menyangkut menyangkut
kepentingan kepentingan umum umum yang yang merefer merefer kepada kepada kebijakan kebijakanotoritas otoritas
pemerintahan pemerintahan. ( . (Codes is a body of laws arranged Codes is a body of laws arranged
systimatically systimatically for easy reference) for easy reference)
2
DEFINISI DEFINISI
nn Specification Specification ((spesifikasi spesifikasi) ) adalah adalah suatu suatu
standard yang standard yang berisikan berisikan penjelasan penjelasan yang yang rinci rinci
dan dan akurat akurat tentang tentang persyaratan persyaratan teknis teknis dari dari
material, material, produk produk, , sistim sistim atau atau jasa jasa..
nn Contoh Contoh Kode Kode ::
Structural Welding Code Structural Welding Code--Steel (AWS D1.1) Steel (AWS D1.1)
Boiler & Pressure Vessel Code (ASME) Boiler & Pressure Vessel Code (ASME)
Welded Pipeline & Vessel (API) Welded Pipeline & Vessel (API)
nn Contoh Contoh Specification : Specification :
Filler Metal Specification (AWS A5.X) Filler Metal Specification (AWS A5.X)
Material & Consumable of Welding (ASME sec. IIC) Material & Consumable of Welding (ASME sec. IIC)
AWS AWS Structural Welding Code Structural Welding Code
nn AWS D l.1, Structural Welding Code AWS D l.1, Structural Welding CodeSteel Steel
nn AWS D l.2, Structural Welding Code AWS D l.2, Structural Welding CodeAluminum Aluminum
nn AWS D l.3, Structural Welding Code AWS D l.3, Structural Welding CodeSheet Steel Sheet Steel
nn AWS D l.4, Structural Welding Code AWS D l.4, Structural Welding CodeReinforcing Steel Reinforcing Steel
nn AWS D l.5, Bridge Welding Code AWS D l.5, Bridge Welding Code
nn AWS D l.6, Structural Welding Code AWS D l.6, Structural Welding CodeStainless Steel Stainless Steel
3
Welding Code Steel (AWS D.1.1)
4
5
ASME STANDARD
API - STANDARD
nn API 1104, Standard for Welding Pipeline API 1104, Standard for Welding Pipeline
and Related Facilities and Related Facilities
nn API 620, Recommended Rules for Design API 620, Recommended Rules for Design
and Construction of Large Welded Low and Construction of Large Welded Low--
Pressure Storage Tanks Pressure Storage Tanks
nn API 650, Standard for Welded Steel Tank API 650, Standard for Welded Steel Tank
for Oil Storage for Oil Storage
6
Persyaratan Persyaratan Dasar Dasar dalam dalam Menentukan Menentukan
Kualitas Kualitas dalam dalam Pengelasan Pengelasan
Standar Standar Eropa Eropa dan dan Amerika Amerika
dalam dalam mendukung mendukung Kualitas Kualitas Lasan Lasan
nn ASME (American Society of Mechanical ASME (American Society of Mechanical
Engineers) Engineers)
nn EN (European Norm) / European Standard EN (European Norm) / European Standard
nn AWS (American Welding Society ) AWS (American Welding Society )
7
ASME Standard ASME Standard untuk untuk Welding Welding
nn ASME Sec IX (Qualification Standard for ASME Sec IX (Qualification Standard for
Welding and Brazing Procedure, Welder, Welding and Brazing Procedure, Welder,
and Welding & Braze Operator. and Welding & Braze Operator.
nn ASME Sec II C Standard for Material and ASME Sec II C Standard for Material and
Consumable of Welding. Consumable of Welding.
STANDARD KUALITAS LAS STANDARD KUALITAS LAS dari dari ASME ASME
Quality of
Welds
Basic Construction Code / Standard :
ASME Sec I, ASME B31.1 , ASME B31.3
ASME Sec VIII Div I & 2
Basic Construction Code / Standard :
ASME Sec I, ASME B31.1 , ASME B31.3
ASME Sec VIII Div I & 2
Welding Personnel
And Welding
Procedure
ASME IX
Welding Personnel
And Welding
Procedure
ASME IX
Welding Material
ASME II C
Welding Material
ASME II C
Examination and
Testing
ASME V
Examination and
Testing
ASME V
8
European Standard For Welding European Standard For Welding
nn EN 288 (Standard & Qualification Welding EN 288 (Standard & Qualification Welding
Procedure) Procedure)
nn EN 287 ( Standard & Qualification of EN 287 ( Standard & Qualification of
Welder) Welder)
nn EN 1418 ( Standard & Qualification of EN 1418 ( Standard & Qualification of
Welding Operator ) Welding Operator )
STANDARD KUALITAS LAS STANDARD KUALITAS LAS dari dari EN EN
9
PROSEDUR LAS PROSEDUR LAS - - EN 288 EN 288
nn EN 288 EN 288 -- 1 . General rules fusion welding. 1 . General rules fusion welding.
nn EN 288 EN 288 -- 2. WPS for Arc Welding 2. WPS for Arc Welding
nn EN 288 EN 288 -- 3. Welding procedure test for Arc welding of 3. Welding procedure test for Arc welding of
steel. steel.
nn EN 288 EN 288 -- 4. Welding Procedure Test for Arc welding 4. Welding Procedure Test for Arc welding
of Aluminum and It of Aluminum and Its alloys s alloys
nn EN 288 EN 288 -- 5. Approval by using approved welding 5. Approval by using approved welding
consumables for arc welding consumables for arc welding
nn EN 288 EN 288 -- 6. Approval related to previous experience 6. Approval related to previous experience
nn EN 288 EN 288 -- 7. Approval by a standard welding procedure 7. Approval by a standard welding procedure
for arc welding for arc welding
nn EN 288 EN 288 -- 8. Approval by a pre 8. Approval by a pre--production welding test. production welding test.
KUALIFIKASI WELDER KUALIFIKASI WELDER - - EN 287 EN 287
nn EN 287 EN 287 -- 1 . Approval testing of welders 1 . Approval testing of welders Fusion welding Fusion welding
part 1 : Steels. part 1 : Steels.
nn EN 287 EN 287 -- 2. Approval testing of welders 2. Approval testing of welders Fusion welding Fusion welding
part 2 : Aluminum and aluminum Alloys. part 2 : Aluminum and aluminum Alloys.
nn EN 287 EN 287 -- 3. Approval testing of welders 3. Approval testing of welders Fusion welding Fusion welding
part 3 : Copper and Copper Alloys. part 3 : Copper and Copper Alloys.
nn EN 287 EN 287 -- 4. Approval testing of welders 4. Approval testing of welders Fusion welding Fusion welding
part 4 : Nickel and Nickels alloys part 4 : Nickel and Nickels alloys
nn EN 287 EN 287 -- 5. Approval testing of welders 5. Approval testing of welders Fusion welding Fusion welding
part 5 : Titanium and Titanium, Zirconium and Zirconium part 5 : Titanium and Titanium, Zirconium and Zirconium
alloys alloys
nn EN 288 EN 288 -- 6. Approval related to previous experience 6. Approval related to previous experience
nn EN 288 EN 288 -- 7. Approval by a standard welding procedure for arc 7. Approval by a standard welding procedure for arc
welding welding
nn EN 288 EN 288 -- 8. Approval by a pre 8. Approval by a pre--production welding test. production welding test.
10
Table 1 Examples of application codes and standards and related welding procedure and welder approval standards
BS EN 287
BS EN 287
ASME IX
BS EN 288 (Parts 3 & 4)
BS EN 288 (Parts 3 & 4)
ASME IX
BS 2654
BS 2594
API 620/650
Storage
Tanks
AWS D1.1
AWS D1.2
BS EN 287
BS EN 287
BS 4872
AWS D1.1
AWS D1.2
BS EN 288 (Part 3)
BS EN 288 (Part 4)
AWS D1.1
AWS D1.2
BS 5135
BS 8118
Structural
Fabrication
BS EN 287 (Part 1)
BS EN 287 (Part 2)
ASME IX
ASME IX
BS 4872/BS EN 287
BS EN 288 (Part 3)
BS EN 288 (Part 4)
ASME IX
ASME IX
BS EN 288 (Part 3)
(if required)
BS 2633
BS 4677
ANSI/ASME B311
ANSI/ASME
B31.3
BS 2971
Process
Pipe-work
BS EN 287
ASME IX
BS EN 288
ASME IX
BS 5500
ASME VIII
Pressure
Vessels
Welder
approval
Procedure
approval
Application
code/standard
Application
Welding Standard
A weld cannot be checked to the full extent !
strength, ductility and corrosion resistance can
only be checked by destructive techniques.
properties can only be guaranteed for the
actual product when manufactured to
exactly the same written procedure,
and carefully controlled.
Why Why a WPS a WPS
11
Why Why a WPS a WPS
The main objective of a
WPS is to make a
welding operation
reproducable
What is What is a a WPS ? WPS ?
The welding procedure is somewhat
analogous to a cook's recipe.
It outlines the steps required to make a quality
weld under specific conditions.
The WPS is a communication tool, and it is the
primary means of communication to all the
parties involved regarding how the welding is
to be performed.
It must therefore be readily available to
foremen, inspectors and the welders.
12
What is What is a a WPS ? WPS ?
According to QW-100.1 ASME Sec IX.
Welding Procedure Specification (WPS).
WPS is a written document that provides direction to the
welder or welding operator for making production welds
in accordance with Code requirements.
According to QW-200.2 ASME Sec IX.
Procedure Qualification Record (PQR).
A PQR is a record of the welding data used to weld a test
coupon. The PQR is a record of variables recorded
during the welding of the test coupons. It also contains
the test results of the tested specimens. Recorded
variables normally fall within a small range of the actual
variables that will be used in production welding.
What is What is WPS Variables ? WPS Variables ?
Process (SMAW, FCAW, etc.)
Electrode specification (AWS A5.1, A5.20, etc.)
Electrode classification (E7018, E71T-1, etc.)
Electrode diameter (1/8 in., 5/32 in., etc.)
Electrical characteristics (AC, DC+, DC-)
Base metal specification (A36, A572 Gr50, etc.)
Minimum preheat and interpass
temperature
Welding current (amperage)/wire feed speed
Arc voltage
Travel speed
Position of welding
Post weld heat treatment
Shielding gas type and flow rate
Joint design details
13
What is What is Variales in WPS ? Variales in WPS ?
1. Essential Variable :
QW-401.1 Essential Variable (Procedure).
A change in a welding condition which will affect the
mechanical properties (other than notch toughness) of the
weldment (for example, change in P-Number, welding
process, filler metal, electrode, preheat or postweld heat
treatment, etc.).
QW-401.2 Essential Variable (Performance).
A change in a welding condition which will affect the
ability of a welder to deposit sound weld metal (such as a
change in welding process, deletion of backing, electrode,
F-Number, technique, etc.).
What is What is Variales in WPS ? Variales in WPS ?
2. Supplemental Essential Variable :
QW-401.3 Supplemental Essential Variable (Procedure).
A change in a welding condition which will affect the notch-
toughness properties of a weldment (for example, change in
welding process, uphill or down vertical welding, heat input,
preheat or PWHT, etc.).
When a procedure has been previously qualified to satisfy all
requirements other than notch toughness, it is then necessary
only to prepare an additional test coupon using the same
procedure with the same essential variables, but additionally
with all of the required
supplementary essential variables, with the coupon long
enough to provide the necessary notch-toughness specimens.
14
What is What is Variales in WPS ? Variales in WPS ?
3. Nonessential Variable :
QW-401.4 Nonessential Variable (Procedure).
A change in a welding condition which will not affect the
mechanical properties of a weldment (such as joint design,
method of back gouging or cleaning, etc.)
15
ASME SECTI ON I X MATERI AL GROUPI NG P-NUMBERS
The material group are based on comparable base material
characteristics, such as composition, weldability, braze-ability,
and mechanical properties.
16
10 Sub Groups:- Mixed bag of high strength low alloy steels. ? 11B
Mixed bag of high strength low alloy steels. ?
11 A Groups 2 to
5
9 Nickel Steels 7 11A Group 1
Typically 26 Chrome one moly ? 10J
Duplex and Super Duplex Grades 31803, 32750 10 10 H
Mixed bag of low alloy steels, 10G 36 Nickel Steel ? 10A,B,C,F,G
Typically two to four percent Nickel Steels 7 9A, B, C
Group 4 Typically 254 SMO type steels
Group 3 High manganese grades
Group 2 Typically Grades 309, 310
Group1 Typically Grades 304, 316, 347
Austenitic Stainless Steels, 4 Sub groups
9 8
Ferritic Stainless Steels Typically Grade 409 8 7
6 Sub Groups:-Martensitic Stainless Steels Typically Grade 410 8 6
5 Sub Groups:-Chrome moly vanadium 6 5C
2 Sub Groups:- Typically five chrome half molyand nine chrome
one moly
5 5B
Typically two and a quarter chrome one moly 5 5A
2 Sub Groups:- Typically one and a quarter chrome half moly 5 4
3 Sub Groups:- Typically half molyand half chrome half moly 4 3
Not Used - 2
Group 4 Special (e.g. SA-724 gr. A, B, C)
Group 3 Approx 80ksi
Group 2 Approx 70ksi
Group 1 up to approx 65 ksi
Carbon Manganese Steels, 4 Sub Groups
1 1
BaseMetal EN-288 P No.
ASME & EN
MATERIAL
P NUMBER
ASME F Numbers
Hard Facing Overlay 7X
Zirconium 6X
Titanium 5X
Nickel alloys 4X
Copper and its alloys 3X
Aluminium and its alloys 2X
Any steel solid or cored wire (with flux or metal) 6
High alloy austenitic stainless steel and duplex :- A5.4 : E316L-16 5
Basic coated electrodes such as : A5.1 : E7016 and E7018 4
Cellulosic electrodes such as :- A5.1 : E6011 3
Most Rutile consumables such as :- A5.1 : E6013 2
Heavy rutile coated iron powder electrodes :- A5.1 : E7024 1
General Description F No.
Note:- X represents any number 0 to 9
17
ASME Welding Positions
Note the welding progression, (vertically upwards or downwards), must always be stated and it is an essential variable for
both procedures and performance qualifications.
Welding Positions For Groove welds:-
JL045 6G Pipe Fixed @ 45 degrees Downwards
HL045 6G Pipe Fixed @ 45 degrees Upwards
PF 5G Pipe Fixed Horizontal
PE 4G Overhead
PG 3G Vertical Downwards Progression
PF 3G Vertical Upwards Progression
PC 2G Horizontal
PA 1G Flat
ISO and EN Test Position Welding Position
Welding Positions For Fillet welds:-
PF 5F Pipe Fixed Horizontal
PD 4F Overhead
PG 3F Vertical Downwards Progression
PF 3F Vertical Upwards Progression
PB 2FR Horizontal Rotated
PB 2F Horizontal
PA 1F Flat (Weld flat joint at 45 degrees)
ISO and EN Test Position Welding Position
POSISI LAS POSISI LAS - - ASME IX ASME IX
18
ASME
WELDING
POSITION
POSISI LAS POSISI LAS - - EN 288 EN 288
19
WELD
POSITION
EN-287
POSISI LAS POSISI LAS - - AWS AWS
20
W
E
L
D
I
N
G
A
N
D
J
O
I
N
I
N
G
..
M
a
n
u
f
a
c
t
u
r
e
r
W
e
l
d
i
n
g
I
n
s
p
e
c
t
W
e
l
d
e
r
W
e
l
d
i
n
g
E
n
g
P
r
o
j
e
c
t
E
n
g
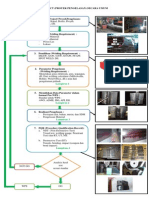
CONTOH TAHAPAN PROSES CONTOH TAHAPAN PROSES
PENGELASAN PIPA PENGELASAN PIPA
..
Welding Application
Welding Application
WPS
WPS
WPQR
WPQR
Inspection
Inspection
Operation
Requirement
Operation
Requirement
Material
Selection
Material
Selection
Fabrication
of Pipes
Fabrication
of Pipes
Science
Standard
Technology
W
E
L
D
I
N
G
A
N
D
J
O
I
N
I
N
G
WELDING PROCEDURES WELDING PROCEDURES
WPQR AND WPS WPQR AND WPS
nn Kualifikasi Kualifikasi Prosedur Prosedur (Procedure Qualification) (Procedure Qualification)
Sebelum mengelas komponen (pipa atau lainnya) umumnya
prosedur pengelasan (welding procedure) harus dibuat dan
dikualifikasi.
nn Dokumentasi Dokumentasi (Record) (Record)
Detail mengenai prosedur harus didokumentasi (record) yang berisi
hasil lengkaptentang procedure qualification test.
nn Kualifikasi Kualifikasi Operator Las (Qualification of Welders) Operator Las (Qualification of Welders)
Setiap welder atau operator las harus dikualifikasi menurut
prosedur baku sebelum melakukan pengelasan komponen (pipa
atau lainnya). Tujuannya adalah untuk menentukan kemampuan
operator las (welder) dalammenghasilkan lasan yang baik tanpa
cacat dengan menggunakan prosedur sebelumnyayang telah lulus
qualifikasi.
21
W
E
L
D
I
N
G
A
N
D
J
O
I
N
I
N
G
I SI WELDI NG PROSEDUR I SI WELDI NG PROSEDUR
WPQR AND WPS WPQR AND WPS
Process Manual, Semi-or
automatic welding process
Pipe and Fitting Material API
5L or ASTM
Diameter and Wall Thickness
Joint Design
Filler Metal and Number of Bed
The size and classification
number of the filler metal and
minimum number and sequence
of bead
Electrical Characteristics The
range of voltage and amperage
Position Roll or fix
Direction of Welding Uphill or
downhill
Time Between Passes Max
time between completion of the
root bed and start of the second
and other bed
Type and Remove of Lineup
Clamp
Cleaning and or Grinding
Pre and Post-Heat Treatment
Methods, Temp. temp-control
methods
Shielding Gas and Flow Rate
Composition and range of flow
rate
Shielding Flux
Speed of Travel in inch per
minute
W
E
L
D
I
N
G
A
N
D
J
O
I
N
I
N
G
CONTOH PENGELASAN PI PA CONTOH PENGELASAN PI PA
NUMBER OF WELD METAL-LAYER
n The number of weld metal-layer (pass) in welding of pipe depend on
pipe wall thickness. Recommended number of layer as shown below.
5/ 8 to 7/ 8 in 3 1
2
3 1 = Root pass
2 = Hott pass
3 = Cover pass
3/ 8 to 5/ 8 in 2 1
2 1 = Rott pass
2 = Cover pass
Range of Pipe
Wall Thickness
Cross Section of Weld
Number
of Layers
Remark
7/ 8 to 1 1/ 8
in
4
1
2
3
4 1 = Root pass
2 = Hott pass
3 = Filler pass
4 = Cover pass
22
W
E
L
D
I
N
G
A
N
D
J
O
I
N
I
N
G
PI PE WELDI NG PROCEDURES PI PE WELDI NG PROCEDURES
TYPE OF PASS
..
Root/ Stringer Bead
5/ 32 Electrode
135 - 175 A DC +
Hot Pass
5/ 32 Electrode
170 - 200 A DC +
Filler Pass
3/ 16 Electrode
180 - 190 A DC +
Cover Pass
3/ 16 Electrode
160 - 190 A DC +
Base Metal
W
E
L
D
I
N
G
A
N
D
J
O
I
N
I
N
G
PI PE WELDI NG PROCEDURES PI PE WELDI NG PROCEDURES
SPEED OF TRAVEL
.
Layer
Travel Speed,
Cm/Minute
Root Pass
Hot Pass
Filler Pass
Cover Pass
7.5 - 20
7.5 - 20
12.5 - 25
12.5 - 25
23
W
E
L
D
I
N
G
A
N
D
J
O
I
N
I
N
G
PI PE WELDI NG PROCEDURES PI PE WELDI NG PROCEDURES
FI LLER METAL
..
Group Electrode
AWS
Specificatio
n
1
A5.1 E6010, E6011
A5.5 E7010, E7011
2 A5.5 E8010, E8011
3
A5.1 or 5.5 E7015, E7016, E7018
A5.5 E8015, E8016, E8018
4
EL8, EL8K, EL12, EM5K A5.17
EM12K, EM13K, EM15K
Electrode
Dia, I n
Votage,
Arc Volt
Current
A
40 - 80
75 - 125
110 - 170
140 - 215
170 - 250
210 - 320
275 - 425
3/ 32
1/ 8
5/ 32
3/ 16
7/ 32
1/ 4
5/ 16
23 - 25
24 -
26
24 - 26
26 - 30
26 - 30
28 - 34
28 - 34
Filler Metal Group AWS E6010 AND E6011
W
E
L
D
I
N
G
A
N
D
J
O
I
N
I
N
G
PI PE WELDI NG PROCEDURES PI PE WELDI NG PROCEDURES
PRE HEATI NG AND STRESS RELI EF
n Preheating shall be performing when:
Carbon steel having a carbon content in
excess of 0.32 % (ladle analysis) or a
carbon equivalent (C + 1/ 4 ( Mn + Si ))
in excess of 0.65 % (ladle analysis).
Steel having lower carbon content or CE
when the welding procedure indicates
that chemical composition, ambient/ or
metal temperature, material thickness
or weld geometry require such
treatment to produce satisfactory welds
(Source ASME B31.8)
n Preheating Method
Furnace Heat Treatment
Induction Heating
Torch Heating
Resistance Heating
Exothermal Heating
..
CE
%
Preheating Reaquired
Up to 0.45
0.45 to 0.60
Over 0.60
Preheat optional
Preheat to 93 - 205 deg C
Preheat to 205 to 370 deg C
Preheating Requirement Based on CE
C Content, % Preheating Temperatur,
o
C
Below 0.2
0.20 - 0.30
0.30 - 0.45
0.45 - 0.80
Up to 93
93 - 150
150 - 260
260 - 425
Preheating Requirement Based on C Content
24
W
E
L
D
I
N
G
A
N
D
J
O
I
N
I
N
G
PI PE WELDI NG PROCEDURES PI PE WELDI NG PROCEDURES
PRE HEATING AND STRESS RELIEFING
Stress - Reliefing
To eliminate or greatly reduce built
up stress caused by welding.
Required when
Following a welding operation on a big
work piece (wall thickness >)
On that is likely to have large built up
stress in it,
Having trouble with work-piece
warping out of shape.
Methods of Stress Relieving
Heat the complete structure as a unit
Heat a complete section containing the
weld to be stress relief
Heat a part of work by slowly heating a
circumferential band containing the
weld at the center.
Branch or other welded attachment
Equipment
Electric induction
Electric resistance
Fuel-fired ring burner
Fuel-fired torch
Temperature Controller
Thermocouple pyrometer
Metal Temp.
o
C
Time per I nch of Section
Thickness, h
593
565
538
510
482
1
2
3
5
10
Stress-Relief Time & Temperature for Carbon
Steel
W
E
L
D
I
N
G
A
N
D
J
O
I
N
I
N
G
PI PE WELDI NG I NSPECTI ON
METHODS OF INSPECTION
NDT
n Visual
n Radiographic Testing
n Magnetic Particle Testing
n Liquid Penetrant Testing
n Ultrasonic Testing
The method used shall produce
indications of defects that can be
accurately interpreted and evaluated.
Qualification of I nspection Personnel
n Welding inspection personnel shall
be qualified by experience and
training for the specified
inspection task they performed.
Radiographic testing performed at
least by Level I
Only Level I I or I I I personnel shall
interprete test results.
Percentages of each days field butt
weld, at randomly by operators
n Class 1 location, except offshore,
at least 10 %
n Class 2 location, at least 15 %
n Class 3, and class 4 location, at
crossing or navigable river,
offshore and rail road or public
highway right of way, including
tunnels, bridges and over head
road crossing, 100 %, unless
impracticable, at least 90 %.
n Pipelines tie-in, 100 %
25
W
E
L
D
I
N
G
A
N
D
J
O
I
N
I
N
G
PIPE WELDING INSPECTION
BASIC CONCEPT
Preparation
Preparation
Acceptance
Acceptance
I nterpretation
and Evaluation
I nterpretation
and Evaluation
Radiographic
Test
Radiographic
Test
Welding is Perfect
Welding is Perfect Repair
Repair
Yes
No
W
E
L
D
I
N
G
A
N
D
J
O
I
N
I
N
G
TerimaKasih
..
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Apa Itu Standard CodeDokumen3 halamanApa Itu Standard CodeAhmad Dzulfiqar RahmanBelum ada peringkat
- Tugas 7 - 1606904951 - Ikhlashia Nur FadhilahDokumen10 halamanTugas 7 - 1606904951 - Ikhlashia Nur FadhilahIkhlashainfBelum ada peringkat
- General Word Welding TecknologieDokumen50 halamanGeneral Word Welding TecknologieAndrey Heynierd TaihuttuBelum ada peringkat
- 06 WPS WelderQual Rev1Dokumen37 halaman06 WPS WelderQual Rev1David JendraBelum ada peringkat
- Tugas-15-Muhammad Ariya AfifDokumen9 halamanTugas-15-Muhammad Ariya Afifariya afifBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 15 Welding MetallurgyDokumen12 halamanChapter 15 Welding MetallurgyMuhammad Ibkar Yusran AsfarBelum ada peringkat
- Kuliah PM Ke-14 Wps-Pqr-CodeDokumen76 halamanKuliah PM Ke-14 Wps-Pqr-CodeRasyad SyachBelum ada peringkat
- TUGAS 7 1406532791 Muhammad FathurrahmanDokumen14 halamanTUGAS 7 1406532791 Muhammad FathurrahmanFathurRahmanBelum ada peringkat
- Tugas Welding 7aDokumen14 halamanTugas Welding 7aDewi Lestari Natalia Marpaung100% (1)
- Tugas Inspeksi Visual 4422201002Dokumen9 halamanTugas Inspeksi Visual 4422201002celindycamellaBelum ada peringkat
- Welding Procedure & Welder QualificationDokumen45 halamanWelding Procedure & Welder QualificationNida I. Farihah100% (6)
- 5 - WELDING PROCEDURE - WELDER QUALIFICATION - 2018 - Rev. 1Dokumen33 halaman5 - WELDING PROCEDURE - WELDER QUALIFICATION - 2018 - Rev. 1Rinaldy SimatupangBelum ada peringkat
- Iso 15607Dokumen13 halamanIso 15607SarjitoBelum ada peringkat
- Pengelasan CodeDokumen3 halamanPengelasan CodeMuh RenandaBelum ada peringkat
- WPS Asme IxDokumen35 halamanWPS Asme IxKennedi Pangaribuan100% (1)
- Welding Procedure & Welder QualificationDokumen45 halamanWelding Procedure & Welder Qualificationluckman231100% (2)
- Pengenalan Standard Code Untuk EngineerDokumen4 halamanPengenalan Standard Code Untuk EngineerafinaBelum ada peringkat
- 00 WPQ Certificate VerificationDokumen25 halaman00 WPQ Certificate VerificationAriq WahyudiBelum ada peringkat
- Bahan Test Kerja QCDokumen8 halamanBahan Test Kerja QCMuslim Ali100% (1)
- WPS Asme IxDokumen35 halamanWPS Asme IxKennedi Pangaribuan33% (3)
- WELDING PROCEDURE - WELDER QUALIFICATION - 2018 - Rev. 1Dokumen33 halamanWELDING PROCEDURE - WELDER QUALIFICATION - 2018 - Rev. 1khamdanBelum ada peringkat
- Binar Satrio Sutardi - 0420035 - UTS Inspeksi LASDokumen5 halamanBinar Satrio Sutardi - 0420035 - UTS Inspeksi LASBinar SatrioBelum ada peringkat
- Welding Code and Standard-2015Dokumen37 halamanWelding Code and Standard-2015Axl Pujangga KelanaBelum ada peringkat
- Standart Asme & APIDokumen3 halamanStandart Asme & APIOllenkBelum ada peringkat
- Tugas WeldingDokumen17 halamanTugas WeldingJuliadi Jawir100% (1)
- Silabus Pelatihan WIDokumen2 halamanSilabus Pelatihan WIsutrimo ir100% (1)
- Quality Assurance of Welding InspectionDokumen67 halamanQuality Assurance of Welding InspectionCandy Kendee100% (4)
- Shabrina Rizky Pratiwi - Tugas 7 - 1606871133Dokumen5 halamanShabrina Rizky Pratiwi - Tugas 7 - 1606871133AgusIsnadiBelum ada peringkat
- Tugas 14Dokumen10 halamanTugas 14Sri Ramayanti Simanjuntak100% (1)
- Inspeksi LasDokumen48 halamanInspeksi LasDaryanto Gultom100% (3)
- Tugas 7 - 1606879395 - Billal Gaung MahardikaDokumen9 halamanTugas 7 - 1606879395 - Billal Gaung MahardikaBilal MahardikaBelum ada peringkat
- Welding QualificationDokumen27 halamanWelding QualificationHari Chairul Zuhud100% (1)
- Rangkuman Asme Sect 9Dokumen40 halamanRangkuman Asme Sect 9Kennedi Pangaribuan0% (1)
- Sampah SIngkatanDokumen23 halamanSampah SIngkatanlaurensiusedoBelum ada peringkat
- Sampah SIngkatan 2Dokumen36 halamanSampah SIngkatan 2laurensiusedoBelum ada peringkat
- Tjgp-Wtip-Qc-Pla-E001 Inspection and Test Plan (Itp) For Piping Afc-0Dokumen25 halamanTjgp-Wtip-Qc-Pla-E001 Inspection and Test Plan (Itp) For Piping Afc-0laurensiusedoBelum ada peringkat
- Tugas 7-1606830070Dokumen11 halamanTugas 7-1606830070noniasliBelum ada peringkat
- Tugas-7 Andy Kurnia W 1606838956Dokumen9 halamanTugas-7 Andy Kurnia W 1606838956Adeline MargaretBelum ada peringkat
- WPSDokumen2 halamanWPSAliNurRahman100% (1)
- Wi Hari Ke-1Dokumen7 halamanWi Hari Ke-1Fhadila AldivaBelum ada peringkat
- Dasar Dasar WPSDokumen83 halamanDasar Dasar WPSTri Sutrisno100% (1)
- Standart PengelasanDokumen10 halamanStandart Pengelasanzuhdan zamzamiBelum ada peringkat
- Standar Dan KodeDokumen9 halamanStandar Dan KodePutra PerdanaBelum ada peringkat
- Tugas Las 1Dokumen3 halamanTugas Las 1Andika Pandu VidiantoBelum ada peringkat
- Presentasi Sambungan FilletDokumen70 halamanPresentasi Sambungan FilletZaenal AbidinBelum ada peringkat
- Resume Pengelasan Mesin Kapal - Wahyu Ramadhan - 40040420650048Dokumen3 halamanResume Pengelasan Mesin Kapal - Wahyu Ramadhan - 40040420650048Wahyu RamadhanBelum ada peringkat
- Menyelesaikan Proyek Pengelasan Secara UmumDokumen23 halamanMenyelesaikan Proyek Pengelasan Secara UmumAvebFrederiksen100% (1)
- Steel Tank SpecificationDokumen12 halamanSteel Tank Specificationarachman297988100% (1)
- TUGAS-14 1906382864 Muhammad Razaqa PerwiranegaraDokumen5 halamanTUGAS-14 1906382864 Muhammad Razaqa PerwiranegaraMuhammad Razaka Perwira NegaraBelum ada peringkat
- ASME VIII DivDokumen2 halamanASME VIII DivInes WidhiBelum ada peringkat
- WeldrfghjkDokumen7 halamanWeldrfghjkRakanBelum ada peringkat
- As MeDokumen40 halamanAs MeRiky RamadhanBelum ada peringkat
- About WelderDokumen3 halamanAbout Welderhrd rodajayasaktiBelum ada peringkat
- Kode Dan Standard Yang Digunakan Pada Industri Proses-1Dokumen8 halamanKode Dan Standard Yang Digunakan Pada Industri Proses-1Muh Arfandi Fatahuddin MBelum ada peringkat
- Jawaban No. 5Dokumen9 halamanJawaban No. 5SE ProductionBelum ada peringkat
- Aws D1.1.Dokumen6 halamanAws D1.1.Reza nugrahaBelum ada peringkat
- Pengertian Boiler Dan Bejana TekanboilerDokumen16 halamanPengertian Boiler Dan Bejana TekanboilerMay HendraBelum ada peringkat
- Perlakuan PanasDokumen8 halamanPerlakuan PanasMay HendraBelum ada peringkat
- PLC2Dokumen7 halamanPLC2May HendraBelum ada peringkat
- Perancangan Mekanisme Mesin Pencetak Batu Bata Merah Kapasitas 8 Buah Per MenitDokumen7 halamanPerancangan Mekanisme Mesin Pencetak Batu Bata Merah Kapasitas 8 Buah Per MenitMay HendraBelum ada peringkat