Obat-Obat Sistem Gastrointestinal 2017 - DR - Devi
Diunggah oleh
faiza rahma0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
61 tayangan43 halamanJudul Asli
Obat-obat sistem gastrointestinal 2017 - dr.Devi.pptx
Hak Cipta
© © All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
PPTX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PPTX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
61 tayangan43 halamanObat-Obat Sistem Gastrointestinal 2017 - DR - Devi
Diunggah oleh
faiza rahmaHak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PPTX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Anda di halaman 1dari 43
Obat-obat sistem
gastrointestinal
Devi Usdiana Rosyidah, dr., M. Sc
Pharmacology Department
Medical Faculty of UMS
2017
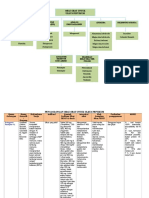
Formularium nasional
Antasida/antiulkus : antasida, esomeprazol,
lansoprazol, omeprazol, ranitidin, sukralfat,
Antiemetik : deksametason, dimenhidrinat,
domperidon, klorpromazin, metoklopramid,
ondansetron,
Antihemoroid : kombinasi
Antispasmodik : atropin, hiosina butilbromid,
Obat diare : atapulgit, garam oralit, kaolin pektin,
loperamid, zinc
Katartik : bisakodil, gliserin, parafin, fenoftalein,
laktulosa, natrium fosfat, polietilen glikol
Lain-lain : asam ursodeoksikolat
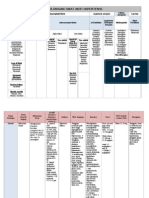
Antasida/antiulkus
Antasida
- Kombinasi : aluminium hidroksida 200
mg+magnesium hidroksida 200 mg tab
kunyah atau suspensi
ANTASID
Basa lemah : Al OH3, Mg OH2, Ca CO3
MK : Mengubah pH lambung, menghambat
pepsin
Dibagi 2 :
a. Sistemik : NaHCO3/Ca
CO3+HClNaCl+H2O+CO2
b. Lokal : AlOH3, MgOH2
ANTASID
ES Antasid sistemik :
- Alkalosis metabolik
- Retensi Na
- Edema
NaHCO3 : alkalinisasi urin, pengobatan pruritus lokal
- Sediaan 500-1000 mg
- Dosis 1-4 gram
Milk alkali syndrom ? NaHCO3/CaCO3 + susu sakit
kepala, iritabel, lemah , mual muntah, K >>>, alkalosis,
kalsifikasi batu di ginjal.
ANTASID
Antasid non sitemik :
- Bersifat demulcen dan adsorben
- Al OH3 : konstipasi
- Indikasi : tuksk peptik, nefrolitiasis fosfat,
adsorben racun
- Sediaan : suspensi, tablet
- Mg OH2 : katartik
ANTASID
CaCoO3: konstipasi, muntah, perdarahan
sal cerna, disfungsi ginjal, fenomena acid
rebound—(sel prietal sekresi
gastrin)sekresi asam lambung saat
malam hari tinggi
Mg2Si3O8nH2O : pembentuk batu
silikatpenggunaan kronik
Sediaan : 500 mg
ANTASID
Ex : NaHCO3, CaCO3distensi abd +
sendawa (pelepasan CO2 dan karbonat)
Mg2+&Al3+abs <<<
Alrelaksasi ot.polos gastrikpenundaan
pengosongan, konstipasi
Mg
Simetikonmenurunkan pembusaan,
turunkan refluk esofagus
Makanan me++ PH jd 5 dlm 1 jam
ANTASID
Mengadsorbsi obat lain
ES :
- Sindrom susu alkali
- Batu ginjal
- Osteomalasia/osteoporosis
- Neurotoksisitas
- Diare
- Na >>>kardiovaskuler disease
- Interaksi : kurangi adsorbsi obat INH, penisilin,
tetrasiklin, nitrofurantoin, as nalidiksat, sulfonamid,
fenilbutazon
ANTASID
Sediaan : 1 produk gabung antara Al OH,
Mg OH dan simetikon
Sering self medication
Hati2 sistemik jangka panjang
suspensi lbh cepat
AH2 : Ranitidin tab 150 mg, injeksi 25
mg/mL
Ex : cimetidin, ranitidin, famotidin,po, iv ;
nizatidin
MK : kompetisi reversibel dg histamin berik. dg
(R) H2X sekresi as.basal, supresi prod. as
o/k makanan, gastrin, hipoglikemia, stimulasi
vagust.u. Nokturnalfrek. 1x/hari sblm
tidur
AH2
FK : abs cepat p.o-ik.prot <<<-ekskresi :
filtrasi, sekresi tub. Ginjal
Durasi kerja iv : cimetidin 4-5 jam, ranitidin
6-8 jam, famotidin 10-12 jam
ES : ringan diare, sakit kepala, mengantuk,
kelelahan, nyeri otot, konstipasi, halusinasi,
delirium, ginekomastia (lk)-ik cimetidin dg
(R) androgen, galaktorea (pr)-X hidroksilasi
estradiol, jml sperma turun/impotensi-
reversibel
Jk panjang ES : sitopenia
AH2
Melalui plasenta, ekskresi ASI(+)
I : ulkus gaster, ulkus duodenal, GERD,
tanpa komplikasi, profilaksis ulkus stress
AH2
SUKRALFAT : tab 500 mg,
suspensi 500 mg/5mL
Td : sukrosa oktasulfat + AlOH2+ Asgel
kental, lengket melekat kuat di sel epitel
selama 6 jam stlh penggunaan
Stimulasi prod PG lokal&EGF
Ikat garam empeduu/esofagitis, gastritis
refluk
Profilaksis ulkus stress
Pemberian saat perut kosong/1 jam sblm
makan, no antasid 30 menit setelah sukralfat
SUKRALFAT
ES : konstipasi , ggn ginjalAl >>>, antasid
(Alumunium/Al), hambat absorbsi obat
lain (oleh karena itu diberikan 2 jam
setelah obat lain)
Anti ulkus : PPI
Esomeprazol serb injeksi 40 mg (iv)
Lansoprazol
a. kaps 30 mgtx jangka pendek tukak lambung,
tukak duodenum, GERD, berikan 1 jam sblm
makan.
b. serb injeksi 30 mgpasien IGD atau rawat inap
dengan riw. Perdarahan sal. cerna
Omeprazol
a. Kaps 20 mgtx jangka pendek tukak lambung,
tukak duodenum, GERD, berikan 1 jam sblm
makan.
b. serb injeksi 40 mgpasien IGD atau rawat inap
dengan riw. Perdarahan sal. cerna
PPI
Paling efektif
Ex : omeprazol 20 mg, esomeprazol,
lansoprazol, rabeprazol, pantoprazol
(tab/iv)
Prodrugaktif (lingk. asam)
Sifat : basa lemah
MK : katalisasi protonberikatan dg
sistein 813ireversibel (24-48 jam/>)
HCl ditekan sd 80-95%
PPI
FK : abs cepat-ik.prot>>>
granul/tablet salut enterik, metab : hati, ekskresi
sulfat : urin, feses, T1/2 1-2 jam, durasi kerja
panjang
Diminum bersamaan/sebelum makan,
interaksi dg antagonis H2
Frek : 1-2x/hari selama 2-5 hari (steady
state)
ES : mual, nyeri abdomen, konstipasi,
flatulensi, diare, atralgia, sakit kepala, ruam,
hipergastronemiahiperplasia sel ECL?
PPI
G T1ok, no teratogenik
Berikan 30 menit sblm makan
I : ulkus gaster, ulkus duodenum, GERD,
sindrom ZE
Antiemetik
Deksametason injeksi 5mg/mL hanya untuk
menyertai terapi antineoplastik
Dimenhidrinat tab 50 mg
Domperidon tab 10 mg, syr 5mg/5mL, drops 5mg/mL
- Modest prokinetic activity in doses of 10-20 mg three
times a day.
- Although it does not readily cross the blood-brain
barrier to cause extrapyramidal side effects,
domperidone exerts effects in the parts of the CNS
that lack this barrier, such as those regulating emesis,
temperature, and prolactin release.
- As is the case with metoclopramide, domperidone
does not appear to have any significant effects on
lower GI motility
Antiemetik
Klorpromazin tab sal 25 mg, injeksi 5
mg/mL (im), injeksi 25 mg/mL (im)
Metoklopramid tab 5 mg, tab 10 mg, syr
5 mg/5 mL, drops 2 mg/mL, injeksi 5
mg/mL
ondansetron tab 4 mg, tab 8 mg, injeksi
2 mg/mL
- Indikasi ondansetron : tab pencegahan
muah dan muntah pd kemoterapi dan
radioterapi, injeksi idem tab yang highly
emetogenik
Antiemetik
Metoclopramide and domperidone are dopamine D 2 -
receptor antagonists.
Within the gastrointestinal tract activation of
dopamine receptors inhibits cholinergic smooth
muscle stimulation; blockade of this effect is believed to
be the primary prokinetic mechanism of action of
these agents.
These agents increase esophageal peristaltic amplitude,
increase lower esophageal sphincter pressure, and
enhance gastric emptying but have no effect on small
intestine or colonic motility.
Metoclopramide and domperidone also block
dopamine D 2 receptors in the chemoreceptor trigger
zone of the medulla (area postrema), resulting in
potent antinausea and antiemetic action
Antiemetik
The most common adverse effects of
metoclopramide involve the central nervous system.
Restlessness, drowsiness, insomnia, anxiety, and
agitation occur in 10–20% of patients, especially the
elderly.
Extrapyramidal effects (dystonias, akathisia,
parkinsonian features) due to central dopamine
receptor blockade occur acutely in 25% of patients
given high doses and in 5% of patients receiving
longterm therapy.
Tardive dyskinesia, sometimes irreversible, has
developed in patients treated for a prolonged period
with metoclopramide.
Antiemetik
For this reason, long-term use should be
avoided unless absolutely necessary,
especially in the elderly.
Elevated prolactin levels (caused by both
metoclopramide and domperidone) can
cause galactorrhea, gynecomastia, impotence,
and menstrual disorders.
Domperidone is extremely well tolerated.
Because it does not cross the blood-brain
barrier to a significant degree,
neuropsychiatric and extrapyramidal effects
are rare
Simeticone
Simethicone is an inert, non-toxic insoluble liquid.
Because of its ability to collapse bubbles by forming a
thin layer on their surface, it is an effective anti-foaming
agent. Although it may be effective in diminishing gas
volumes in the GI tract, it is not clear whether this
accomplishes a therapeutic effect.
Simethicone is available in chewable tablets, liquid-filled
capsules, suspensions, and orally disintegrating strips,
either by itself or in combination with other overthe-
counter medications including antacids and other
digestants.
The usual dosage in adults is 40-25 mg four times daily.
Activated charcoal may also be used alone or in
combination with simethicone, but has not been shown
conclusively to have much benefit
Antiemetik
Antihemoroid
Kombinasi bx supositoria anal : bismut
subgalat, heksaklorofen lidokain, seng
oksida,
Produk lain :
- Baca MIMS/ISO
Antispasmodik
Atropin tab 0,5 mg, injeksi 0,25 mg/mL
(im,iv,sc)
hiosina butilbromid tab 10 mg, injeksi 20
mg/mL
Obat diare
Atapulgit tab
garam oralit
kaolin pektinkaolin 550mg+pektin
20mg
Loperamid tab sal selaput 2 mgtidak
untuk anak-anak
Zinc tab dispersal 20 mg, syr 20mg/5mL,
serb 10 mgdiberikan bersama oralit
selama 10 hari
Obat diare
Pharmacotherapy of diarrhea in adults should be reserved
for patients with significant or persistent symptoms.
Nonspecific anti-diarrheal agents typically do not address
the underlying pathophysiology responsible for the diarrhea;
their principal utility is to provide symptomatic relief in
mild cases of acute diarrhea.
Many of these agents act by decreasing intestinal motility
and should be avoided as much as possible in acute
diarrheal illnesses caused by invasive organisms.
In such cases, these agents may mask the clinical picture,
delay clearance of organisms, and increase the risk of
systemic invasion by the infectious organisms; they also may
induce local complications such as toxic megacolon
Obat diare
Some of these agents also may bind bacterial toxins
and bile salts. Clays such as kaolin (a hydrated
aluminum silicate) and other silicates such as
attapulgite (magnesium aluminum disilicate;
DIASORB, others) bind water avidly (attapulgite
absorbs eight times its weight in water) and also may
bind enterotoxins.
However, binding is not selective and may involve
other drugs and nutrients; hence these agents are
best avoided within 2-3 hours of taking other
medications.
A mixture of kaolin and pectin (a plant
polysaccharide) is a popular over-the-counter
remedy (KAOPECTOLIN, others) and may provide
useful symptomatic relief of mild diarrhea
Loperamid
Loperamide (IMODIUM,IMODIUM A-D, others), a
piperidine butyramide derivative with μreceptor
activity, is an orally active anti-diarrheal agent.
The drug is 40-50 times more potent than
morphine as an anti-diarrheal agent and
penetrates the CNS poorly. It increases small
intestinal and mouth-to-cecum transit times.
Loperamide also increases anal sphincter tone, an
effect that may be of therapeutic value in some
patients who suffer from anal incontinence.
Loperamid
In addition, loperamide has anti-secretory
activity against cholera toxin and some
forms of Escherichia colitoxin, presumably
by acting on Gi-linked receptors and
countering the increase in cellular cyclic
AMP generated in response to the toxins
Overdosage, however, can result in CNS
depression (especially in children) and
paralytic ileus.
Katartik
Bisakodil tab sal 5 mg, susp 5 mg, supositoria
10 mg
Gliserin drops 10mg/mL, cairan obat luar
100mg/mL
Kombinasi : Parafin+gliserin+Fenoftalein
Laktulosa syr 3,335 g/5mL
natrium fosfat lar oral hanya untuk
colonoscopy
polietilen glikol serbuk
Obat konstipasi/pencahar
Pencahar rangsang : minyak jarak,
bisakodil, dll
Pencahar garam : mg sulfat, Na sulfat, dll
Pencahar pembentuk masa : metilselulosa,
agar
Pencahar emolien : parafin cair, minyak
zaitun, dll
Obat konstipasi/pencahar
Obat konstipasi/pencahar
Lain-lain : asam ursodeoksikolat
Cholic acid, chenodeoxycholic acid, and
deoxycholic acid constitute 95% of bile acids;
lithocholic acid and ursodeoxycholic acid are
minor constituents.
Bile acids and their conjugates are essential
components of bile that are synthesized from
cholesterol in the liver.
Lain-lain : asam
ursodeoksikolat
Bile acids were first used therapeutically
for gallstone dissolution; use for this
indication requires a functional gallbladder
because the modified bile must enter the
gallbladder to interact with gallstones. To
be amenable to dissolution, the gallstones
must be composed of cholesterol
monohydrate crystals and generally must
be <15 mm in diameter to provide a
favorable ratio of surface to size.
Lain-lain : asam
ursodeoksikolat
For these reasons, the overall efficacy of
litholytic bile acids in the treatment of
gallstones has been disappointing (partial
dissolution occurs in 40-60% of patients
completing therapy and is complete in only
33-50% of these).
Although a combination of chenodiol and
ursodiol probably is better than either agent
alone, ursodiol is preferred as a single agent
because of its greater efficacy and
lessfrequent side effects (e.g., hepatotoxicity)
Buku rujukan
Formularium nasional tahun 2015
FK UI, 2016. Farmakologi dan terapi.
Jakarta : departemen farmakologi dan
terapi FK UI
Goodman & Gilman’s. 2011. The
Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics.
twelfth edition. New York : Mc-Graw Hill
Katzung, 2012. Basic and clinical
pharmacology. 12th edition. Mc-Graw Hill
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Farmako Digestif (Dr. Fahrul)Dokumen35 halamanFarmako Digestif (Dr. Fahrul)farah maulida martaBelum ada peringkat
- Farmakologi GastrointestinalDokumen42 halamanFarmakologi GastrointestinalwirdahajaBelum ada peringkat
- Minggu XII Farmakologi Sistem PencernaanDokumen65 halamanMinggu XII Farmakologi Sistem PencernaanDiarBelum ada peringkat
- Farmakoterapi DispepsiaDokumen4 halamanFarmakoterapi DispepsiaAmy SingletonBelum ada peringkat
- Obat-Obat Lambung DR DarDokumen37 halamanObat-Obat Lambung DR DarniajaplaniBelum ada peringkat
- Spesialite Obat Saluran CernaDokumen15 halamanSpesialite Obat Saluran CernaFauzan AprnBelum ada peringkat
- FARMAKOLOGI GASTROINTESTINAL Kuliah 1Dokumen62 halamanFARMAKOLOGI GASTROINTESTINAL Kuliah 1Yulia Dewi Aini100% (2)
- FARMAKOLOGI GASTROINTESTINAL Kuliah 1Dokumen62 halamanFARMAKOLOGI GASTROINTESTINAL Kuliah 1Danang RaharjoBelum ada peringkat
- Penatalaksanaan Dan Pencegahan DispepsiaDokumen11 halamanPenatalaksanaan Dan Pencegahan DispepsiaSyifa NurainiBelum ada peringkat
- Farmakologi Obat Saluran CernaDokumen35 halamanFarmakologi Obat Saluran CernaAdhitya Angga KharismaBelum ada peringkat
- Klasifikasi Obat GIT by Dion FaisalDokumen19 halamanKlasifikasi Obat GIT by Dion FaisaldanaBelum ada peringkat
- Obat Obat Saluran CernaDokumen6 halamanObat Obat Saluran Cernadr. NellyBelum ada peringkat
- Obat Saluran CernaDokumen9 halamanObat Saluran CernaDianaku BugisBelum ada peringkat
- Antitukak Peptik Dan LaksansiaDokumen61 halamanAntitukak Peptik Dan LaksansiaSiddiq Blackhell CakepBelum ada peringkat
- 07 Okt 2021 - Obat Saluran Cerna 1 - Spesialit ObatDokumen20 halaman07 Okt 2021 - Obat Saluran Cerna 1 - Spesialit ObatAdel ZilviaBelum ada peringkat
- Tabel Obat DispepsiaDokumen4 halamanTabel Obat DispepsiaElisabet_Anita_1486Belum ada peringkat
- Pert 4. Spesialite Obat Dan Terminologi PD Sist PencernaanDokumen43 halamanPert 4. Spesialite Obat Dan Terminologi PD Sist PencernaanNanang Kedokteran100% (1)
- Klasifikasi Obat GITDokumen18 halamanKlasifikasi Obat GITamaliaturrahmah50% (2)
- Terapi Farmakologi Untuk Penyakit Saluran PencernaanDokumen70 halamanTerapi Farmakologi Untuk Penyakit Saluran PencernaanBRamBelum ada peringkat
- Klasifikasi Obat Anti EpilepsiDokumen4 halamanKlasifikasi Obat Anti EpilepsiAprilini FitrisiaBelum ada peringkat
- Anti EpilepsiDokumen5 halamanAnti EpilepsiamaliaturrahmahBelum ada peringkat
- Kelompok 3 - Ambar Listyorini - Hafizha Fadhila Suleman - Tugas 2 Farmakoterapi ApotekerDokumen37 halamanKelompok 3 - Ambar Listyorini - Hafizha Fadhila Suleman - Tugas 2 Farmakoterapi ApotekerAmbar ListyoriniBelum ada peringkat
- Farmakologi Gastrointestinal Kuliah 1pptDokumen62 halamanFarmakologi Gastrointestinal Kuliah 1pptFitri Ayu WahyuniBelum ada peringkat
- Obat Obat Saluran CernaDokumen4 halamanObat Obat Saluran CernadiyyaBelum ada peringkat
- Referat DomperidoneDokumen10 halamanReferat DomperidoneDewi Muzzayyanti100% (2)
- Analgetik & AntipiretikDokumen40 halamanAnalgetik & AntipiretikanissaflrBelum ada peringkat
- ANTASIDADokumen47 halamanANTASIDAIsnaeni LaiLatun NurBelum ada peringkat
- Obat Sistem PencernaanDokumen21 halamanObat Sistem Pencernaanhasna sabilaBelum ada peringkat
- Farmakologi GastroDokumen33 halamanFarmakologi GastroRa RahmaBelum ada peringkat
- Kasus DispepsiaDokumen16 halamanKasus DispepsiadichynuryadinzainBelum ada peringkat
- Farmakoterapi Gangguan Sistem PencernaanDokumen150 halamanFarmakoterapi Gangguan Sistem PencernaanNaomy OctavinnaBelum ada peringkat
- TugasDokumen16 halamanTugasSeptyaNugrahaBelum ada peringkat
- CIMETIDINEDokumen5 halamanCIMETIDINEWigati NuraeniBelum ada peringkat
- Farmakologi Gangguan NeurologisDokumen21 halamanFarmakologi Gangguan NeurologisIka Wardhani KaruniaBelum ada peringkat
- Antagonis H2Dokumen4 halamanAntagonis H2Herdiko Shalatin100% (1)
- Lamb UngDokumen47 halamanLamb UngGemini AvenueBelum ada peringkat
- AnalgetikDokumen46 halamanAnalgetikAbi FathiBelum ada peringkat
- Obat Obat Saluran CernaDokumen5 halamanObat Obat Saluran Cernabotet_2306Belum ada peringkat
- Kasus Batuk 1Dokumen8 halamanKasus Batuk 1kathy_03Belum ada peringkat
- AntasidaDokumen9 halamanAntasidakriswantiBelum ada peringkat
- TugasDokumen17 halamanTugasZulfikarBelum ada peringkat
- Farmakoterapi Saluran CernaDokumen63 halamanFarmakoterapi Saluran Cernaelva sucia pertiwi100% (1)
- Golongan Antidiabetik OralDokumen4 halamanGolongan Antidiabetik OralFerry Akbar AnisBelum ada peringkat
- Obat Dispepsia, Anti Diare, Dan GERDDokumen13 halamanObat Dispepsia, Anti Diare, Dan GERDNerissaArvianaShintaraBelum ada peringkat
- Contoh Obat ProkinetikDokumen7 halamanContoh Obat ProkinetikLiana FebriantiBelum ada peringkat
- Gastroentero FarmakologiDokumen133 halamanGastroentero FarmakologiKresna Denta ElygioBelum ada peringkat
- Tugas Pak HarisDokumen11 halamanTugas Pak HarisNindi MPBelum ada peringkat
- CIMETIDINEDokumen4 halamanCIMETIDINEbinatanglautBelum ada peringkat
- Antagonis Reseptor H2 FarmaDokumen11 halamanAntagonis Reseptor H2 FarmaIndraArdana100% (1)
- JduakaolahgDokumen27 halamanJduakaolahgDagaboyBelum ada peringkat
- Makalah Obat-Obat LambungDokumen8 halamanMakalah Obat-Obat LambungAtik YuliBelum ada peringkat
- Farmakokinetik Dan FarmakodinamikDokumen11 halamanFarmakokinetik Dan FarmakodinamikMalik Aziz100% (1)
- Peptic UlcerDokumen14 halamanPeptic UlcerMuhammad Jordianda PutraBelum ada peringkat
- Obat BronkodilatorDokumen19 halamanObat BronkodilatorFirani Amazona100% (1)
- Obat Saluran CernaDokumen6 halamanObat Saluran CernaAD MonikaBelum ada peringkat
- Golongan Obat Anti HipertensiDokumen14 halamanGolongan Obat Anti HipertensiADILHARAALCITAMESABelum ada peringkat
- Resep ObatDokumen31 halamanResep ObatErwin MauritzBelum ada peringkat
- Penyakit Tuberkulosis Paru Dan SistemikDokumen55 halamanPenyakit Tuberkulosis Paru Dan SistemikErvina Lie100% (1)
- PerdarahanDokumen3 halamanPerdarahanfaiza rahmaBelum ada peringkat
- KELAINAN ORGAN GENITALIA MATERI KULIAH - DR - Ali SamhurDokumen60 halamanKELAINAN ORGAN GENITALIA MATERI KULIAH - DR - Ali Samhurfaiza rahmaBelum ada peringkat
- Contoh - TB LARING FIX REVISI 31 DESDokumen19 halamanContoh - TB LARING FIX REVISI 31 DESfaiza rahmaBelum ada peringkat
- KELAINAN ORGAN GENITALIA MATERI KULIAH - DR - Ali SamhurDokumen60 halamanKELAINAN ORGAN GENITALIA MATERI KULIAH - DR - Ali Samhurfaiza rahmaBelum ada peringkat
- Diagnosa Dan Penatalaksanaan Asma Berdasarkan GINADokumen33 halamanDiagnosa Dan Penatalaksanaan Asma Berdasarkan GINAfaiza rahmaBelum ada peringkat
- Prinsip OsceDokumen3 halamanPrinsip Osceeko andryBelum ada peringkat
- PATOLOGI PERSALINAN MATERI KULIAH - Dr. Ali SamhurDokumen51 halamanPATOLOGI PERSALINAN MATERI KULIAH - Dr. Ali Samhurfaiza rahmaBelum ada peringkat
- PEMERIKSAAN GINEKOLOGI MATERI KULIAH - Dr. Ali SamhurDokumen44 halamanPEMERIKSAAN GINEKOLOGI MATERI KULIAH - Dr. Ali Samhurfaiza rahmaBelum ada peringkat
- Kuliah 7 Meridian IstimewaDokumen6 halamanKuliah 7 Meridian Istimewafaiza rahmaBelum ada peringkat
- PATOLOGI PERSALINAN MATERI KULIAH - Dr. Ali SamhurDokumen51 halamanPATOLOGI PERSALINAN MATERI KULIAH - Dr. Ali Samhurfaiza rahmaBelum ada peringkat
- PEMERIKSAAN GINEKOLOGI MATERI KULIAH - Dr. Ali SamhurDokumen44 halamanPEMERIKSAAN GINEKOLOGI MATERI KULIAH - Dr. Ali Samhurfaiza rahmaBelum ada peringkat
- Dr. Ali Samhur SP - Og - Pemeriksaan ObstetriDokumen33 halamanDr. Ali Samhur SP - Og - Pemeriksaan ObstetriDhiastikaBelum ada peringkat
- Materi Kuliah III - Peranan Radiologi Pada TraumatologiDokumen56 halamanMateri Kuliah III - Peranan Radiologi Pada TraumatologiAnanto WibisonoBelum ada peringkat
- Fungsi Keluarga - Dr. AnikaDokumen63 halamanFungsi Keluarga - Dr. Anikafaiza rahmaBelum ada peringkat
- Bells PalsyDokumen18 halamanBells PalsySandy MurtiningtyasBelum ada peringkat
- Rational ThrapiDokumen68 halamanRational Thrapifaiza rahmaBelum ada peringkat
- AntimikrobakuDokumen89 halamanAntimikrobakuZammira MutiaBelum ada peringkat
- Imunisasi - Dr. IskandarDokumen38 halamanImunisasi - Dr. Iskandarfaiza rahmaBelum ada peringkat
- AntiamubaDokumen16 halamanAntiamubamariobrosBelum ada peringkat
- Dasar Dasar Kedokteran Komunitas 2017 - Dr. YusufDokumen82 halamanDasar Dasar Kedokteran Komunitas 2017 - Dr. Yusuffaiza rahmaBelum ada peringkat
- Manajemen FASKESDokumen50 halamanManajemen FASKESfaiza rahmaBelum ada peringkat
- Standar Mutu Praktek Kedokteran KeluargaDokumen114 halamanStandar Mutu Praktek Kedokteran KeluargaMuhammad Dony HermawanBelum ada peringkat
- Promosi Kesehatan 2Dokumen35 halamanPromosi Kesehatan 2Muhammad Dony HermawanBelum ada peringkat
- Done ANALISIS-SWOT-PUSKESMASDokumen29 halamanDone ANALISIS-SWOT-PUSKESMASOma ChachaBelum ada peringkat
- Standar Mutu Praktek Kedokteran KeluargaDokumen114 halamanStandar Mutu Praktek Kedokteran KeluargaMuhammad Dony HermawanBelum ada peringkat
- PALLIATIVE CARE - Dr. AnikaDokumen73 halamanPALLIATIVE CARE - Dr. Anikafaiza rahmaBelum ada peringkat
- Manajemen FASKESDokumen50 halamanManajemen FASKESfaiza rahmaBelum ada peringkat
- Gizi MasyarakatDokumen10 halamanGizi MasyarakatMuhammad Dony HermawanBelum ada peringkat
- Fungsi Keluarga - Dr. AnikaDokumen63 halamanFungsi Keluarga - Dr. Anikafaiza rahmaBelum ada peringkat