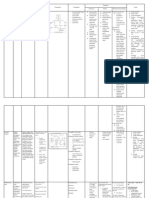
SCARLET FEVER
definisi
Scarlet fever atau scarlatina adalah suatu sindrom yang ditandai oleh faringitis eksudatif, demam,
dan eksantema merah terang. Hal ini disebabkan oleh kelompok penghasil racun group A betahemolytic streptococci (GABHS) ditemukan dalam sekresi dan keluarnya cairan dari hidung,
telinga, tenggorokan, dan kulit.
Biasanya, demam scarlet berkembang dari fokus tonsil / faring, meskipun ruam muncul dalam
waktu kurang dari 10% dari kasus "radang tenggorokan." Situs replikasi bakteri cenderung
mencolok dibandingkan dengan efek dramatis yang disebabkan racun. Infeksi streptokokus
Exotoxin-mediated berkisar dari gangguan kulit lokal (misalnya, impetigo bulosa) sampai erupsi
luas demam scarlet sampai sangat mematikan yaitu streptokokus toxic shock syndrome.
etiologi
Racun eritrogenik yang dihasilkan oleh group A beta-hemolytic streptococci GABHS adalah
penyebab ruam demam scarlet.
epidemiologi
Sebanyak 10% dari populasi terjangkit faringitis streptococcal group A, Dari kelompok ini,
sebanyak 10% terjangkit scarlet fever
Anak usia 5-15 tahun, meskipun juga dapat terjadi pada anak yang lebih tua dan orang dewasa.
Perempuan = laki2
�patofisiologi
Sesuai namanya "scarlet fever", erupsi eritematosa dikaitkan dengan
penyakit demam.
Racun yang diproduksi oleh GABHS dan sering disebut sebagai
racun erythemogenic atau eritrogenik produksi mediator lokal
inflamasi dilatasi pembuluh darah menyebabkan ruam
patognomonik
Biasanya, tempat replikasi GABHS demam scarlet adalah tonsil dan
faring. Klinis tidak dapat dibedakan, demam scarlet dapat disertai
infeksi streptokokus pada kulit dan jaringan lunak, luka bedah
(misalnya, demam berdarah bedah), atau rahim (misalnya, demam
berdarah nifas).
�Gejala klinis
Hampir semua pasien demam Scarlet mengalami nyeri tenggorokan dan ruam
kemerahan. Gejala lain yang sering menyertai penyakit ini adalah sebagai berikut:
1.Ruam
merah di sekitar leher dan dada, lalu meluas ke bagian tubuh yang lain
2.Ruam
di daerah lipatan-lipatan tubuh biasanya lebih gelap sehingga membentuk garis
3.Muka
memerah
4.Lidah
tampak merah dan bertotol-totol dan sering disebut lidah strawberry
merah
5.Demam
hingga 38,8 derajat celcius disertai menggigil
6.Nyeri
tenggorokan disertai radang yang tampak memerah dan bercak luka yang
memutih
7.Susah
menelan
8.Kelenjar
9.Mual,
limpa di leher membengkak
muntah dan sakit kepala.
��komplikasi
Complications of scarlet fever may include the following:
1.Cervical lymphadenitis
2.Otitis media and/or mastoiditis
3.Ethmoiditis
4.Peritonsillar abscess
5.Sinusitis
6.Bronchopneumonia
7.Meningitis
8.Brain abscess
9.Intracranial venous sinus thrombosis
10.Septicemia, meningitis, osteomyelitis, and septic arthritis
11.Acute renal failure from poststreptococcal glomerulonephritis
12.Hepatitis
13.Vasculitis
14.Uveitis
�diagnosis
Pemeriksaan penunjang
In addition to standard blood and urine tests done as part of a complete
medical workup, the following studies are indicated in scarlet fever:
Throat
culture or rapid streptococcal test
Anti-deoxyribonuclease
B and antistreptolysin-O titers (antibodies to
streptococcal extracellular products)
The
complete blood count (CBC) commonly reveals a leukocytosis. The
white blood cell (WBC) count in scarlet fever may increase to 12,00016,000/L, with a differential of up to 95% polymorphonuclear
lymphocytes. During the second week, eosinophilia, as high as 20%, can
develop.
Urinalysis
and liver function tests may reveal changes associated with
complications of scarlet fever. Said tests are part of a complete medical
workup.
�tatalaksana
Penicillin G benzathine (Bicillin LA). Penicillin G interferes with synthesis of
cell wall mucopeptides during active multiplication, which results in bactericidal
activity.
Penicillin VK. Penicillin VK is the drug of choice. It inhibits biosynthesis of cell
wall mucopeptides and is effective during active multiplication. Inadequate
concentrations may produce only bacteriostatic effects.
Amoxicillin (Moxatag). Amoxicillin is an alternative drug of choice. It interferes
with synthesis of cell wall mucopeptides during active multiplication, resulting in
bactericidal activity against susceptible bacteria.
Erythromycin (E.E.S., E-Mycin, Ery-Tab).Erythromycin is the drug of choice in
penicillin-allergic patients. It inhibits bacterial growth, possibly by blocking
dissociation of peptidyl tRNA from ribosomes, causing RNA-dependent protein
synthesis to arrest. It is used for treatment of infections caused by susceptible
strains, including streptococci. In children, age, weight, and severity of infection
determine proper dosage. When twice-daily dosing is desired, half of the total daily
dose may be taken every 12 hours. For more severe infections, double the dose.
Cephalexin (Keflex). Cephalexin is an alternative drug of choice. It is a firstgeneration cephalosporin that arrests bacterial growth by inhibiting bacterial cell
wall synthesis. It has bactericidal activity against rapidly growing organisms. Its
primary activity is against skin flora; it is used for skin infections.
�diagnosa banding
Rubeola
Rubella
Roseola
Demam reumatik
Erisipelas
Erupsi obat
Penyakit kawasaki
Leptospirosis
Virus immunodefisiensi manusia
dll
�sumber
http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1053253-overview
Nelson esensi pediatri edisi 4