Terapi Cairan Pada Syok Hipovolemik
Diunggah oleh
anchemeysDeskripsi Asli:
Judul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Terapi Cairan Pada Syok Hipovolemik
Diunggah oleh
anchemeysHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
TERAPI CAIRAN PADA SYOK
HIPOVOLEMIK
soal
Pasien 32 tahun, datang post
partum, lahir diluar rumahsakit.
Tidak sadar, nafas 10 x/menit, Nadi
tidak teraba, Tensi tidak terukur,
muka pucat Apa yang Sdr
lakukan ?
soal
Pasien 25 tahun, datang ke
rumahsakit akibat KLL. Tidak sadar,
nafas 8 x/menit, Nadi tidak teraba,
Tensi tidak terukur, muka pucat.
Apa yang Sdr lakukan ?
PRINSIP
Terapi keadaan yang paling
mengancam jiwa
Kekurangan untuk diagnosa definitif
tidak mencegah untuk dimulainya
tindakan.
Tidak diperlukan anamnesa lengkap
INGAT:
Hilangnya airway akan menimbulkan
kematian lebih cepat daripada hilangnya
kemampuan bernafas
Hilangnya kemampuan bernafas
menimbulkan kematian lebih cepat dari
hilangnya volume sirkulasi.
Hilangnya volume sirkulasi lebih cepat
menimbulkan kematian daripada
penambahan massa intrakranial
Initial Assessment
Preparation
Triage
Primary survey (ABCDE)
Resuscitation
Secondary survey (head to toe)
Resuscitation
Definitive care
ABCDE
A = Airway with cervical spine control
B = Breathing
C = Circulation
D = Disability or Neurological status
E = Exposure with temperature control
A = Airway and C-Spine
control
Airway harus dinilai paling dulu
Lihat tanda obstruksi jalan nafas :
adanya benda asing, fraktur facial,
mandibula, tracheal/laringeal
Chin-lift, jaw thrust
Hati-hati ada cervical spine fracture
A (lanjutan):
Perkirakan ada C-Spine fracture pada
setiap pasien trauma multisistim
dengan penurunan kesadaran, ada jejas
diatas clavicula.
Inline immobilization
Cegah rotasi, fleksi, extensi kepala.
B = Breathing
Ventilasi memerlukan fungsi adekuat
dari paru, dinding dada dan diafragma.
Cedera yang mengganggu ventilasi
secara akut : tension pneumothoraks,
flail chest dengan contusio paru, open
pneumothoraks, massive hemothoraks.
C = Circulation and
hemorrhage control
Diagnosa cepat untuk kehilangan
volume darah : perubahan kesadaran
dan nadi.
Penurunan kesadaran karena
penurunan CBF
Nadi : frekuensi dan tekanan nadi
Warna kulit : muka abu-abu, extrimitas
pucat
D = neurological evaluation
AVPU
A = Alert
V = responds to Vocal stimuli
P = responds only to Painful stimuli
U = Unresponsive
Pemeriksaan GCS saat primary atau
secondary survey
Resusitasi Jalan Nafas
Jangan hiperektensi dan rotasi kepala
Bila sadar pasang nasofaringeal airway
Bila tidak sadar pasang orofaringeal
airway
Intubasi bila pasien tidak sadar,
gangguan airway, ada masalah ventilasi
Surgical airway: bila tidak bisa
diintubasi, kontra indikasi intubasi
Resusitasi Breathing
Ventilasi dengan face mask
Bila telah diintubasi, ventilasi dengan
ambu bag
Jet ventilasi dengan t-piece
Toraks drain
Chest decompression
Resusitasi Circulation
Pasang jarum vena 2 buah dengan
abocath no 16
Ambil contoh darah
Beri cairan
Pada pasien syok beri RL atau NaCL
Vascular akses
Setiap pasien trauma dewasa pasang
jarum vena, 2 buah, nomor besar (16)
Pasang di vena perifer, bila tidak bisa
pasang divena sentral
Pada anak < 6 tahun, bila tidak bisa
dipasang di vena perifer intraosseous
Intraosseous sifatnya sementara.
Perdarahan
Lakukan balut tekan
Jangan pakai torniket
Hipovolemia/syok kemungkinan besar
dari : perdarahan intraabdominal atau
intratorakal, fraktur femur atau pelvis,
robekan arteri atau vena, perdarahan
external yang luas.
SYOK
Pertama kali tentukan bahwa pasien
dalam keadaan syok
Tahap kedua tentukan penyebab syok
Ingat syok pada cedera kepala, adalah
karena hipovolemik syok ditempat lain
SYOK
Diagnosa syok : bila ada takikardi dan
vasokonstriksi kulit.
Jadi pada pasien trauma asal pasien diraba
dingin dan ada takikardia SYOK
Jangan berdasarkan tekanan darah
Bisa dari tekanan nadi ( Sist Diast), tekanan
nadi sempit kehilangan darah yang nyata
Definisi takikardi
Pada infant > 160
Anak belum sekolah >140
Anak usia sekolah-pubertas > 120
Dewasa > 100
Etiologi syok
Hemorhagic syok
Non hemorhagic syok :
Cardiogenic syok,
Tension pneumothoraks,
Neurogenik syok,
Septik syok.
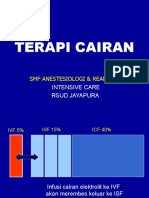
I. PHYSIOLOGY
TOTAL BODY FLUID 60% BW
INTRACELLULAR
FLUID (ICF)
EXTRACELLULAR
FLUID (ECF) 20% BW
TRANSCELLULAR
FLUID
40 % BW
INTRAVASCULAR
FLUID
INTERSTITIIL
FLUID
5 % BW 15 % BW
1-3 % BW
ATLS classification of hemorrhagic
shock
Class I Class II Clas III Class IV
Blood loss (ml)
Blood loss (% of BV)
Heart rate
SBP
Pulse pressure
Capillary refill test
Resp rate
Urine output
Mental status
Fluid replacement
Up to 750
Up to 15%
<100
Normal
Normal or
Normal
14-20
>30
Slightly anxious
Crystalloid
750-1000
15-30%
>100
Normal
Decreased
Positive
20-30
20-30
Mildly anxious
Crystalloid
1500-2000
20-40%
>120
Decreased
Decreased
Positive
30-40
5-25
Anxious and
confused
Crystalloid
and blood
>2000
>40%
>140
Decreased
Decreased
Positive
<35
Negligible
Confused
andlethargic
Crystalloid
and blood
Supine hypo tension deficit > 30%
Orthostatic hypotension blood vol deficit
20%
Young healthy person, 20% deficit postural
tachycardia only
Geriatrics, Cardiovascular reserve
orthostatic hypo tension despite normovolemi
Tilt test
Compare arterial blood pressure value between
supine and sitting position
Asses intravascular volume
Laboratory Test in Shock
Test normal value Suspect
hypovolemia
Limitation
BUN mg% 8- 20 > 20 Renal func
Cr mg% 0,5 - 1,2 > 1,2 Variable Cr prodct
, renal func
BUN/Cr < 20 >20 idem
Na urine meq/l > 30 <20 Renal funct
Osm urine
mosm/l
<800 >400 Renal funct
Lactic acidosis
mmol/l
< 2 > 3 Late sign
Bic nat meq/l 22 - 26 > 26
Terapi syok hipovolemik
Pada dewasa : beri 2-3 liter Rl atau NaCl
0,9% evaluasi
Anak : 20 cc/kg , diulang dua kali, bila tidak
ada respons beri darah.
Darah tipe spesifik, bila tidak ada pack-red
cell O.
Syok hipovolemik jangan diterapi dengan
vasopressor, steroid atau bikarbonat.
Jenis2 cairan untuk mengisi
volume I.vaskuler
Jenis Na Cl K Ca Mg Lact/Aceta
t
lain2
NaCl0.9%
154 154 -
- - - -
Ring Lakt 138 112 4 5
-
Lakt/28
-
Expafusin
138 125 4 3 Lakt/20 HES/40000
Haes st 6%
,10%
154 154
- - - -
HES/200000
Hemacel 145 145 5,1 6,25
- -
Polygeline
Gelafundin 142 80 - 1,4
- -
Gelatin/35000
Dextran L 130 108 4 2,7 - Lakt/28
Dextran40
NaCl 3% 500 500
- - - - -
Crystalloid Colloid
Advantages - Inexpensive
- Promotes urinary
flow
- Fluid of choice for
initial resuscitation
of
trauma/hemorrhage
- Expands
intravascular volume
- Restores 3
rd
spaces
losses
-More sustained intravascular
-Volume increase (1/3 still intravascular at 24 hrs)
- Maintain or increase plasma oncotic pressure
-Requires smaller volume for equal effects
-Less peripheral oedem (more fluids remains
intravascular)
-May lower intracranial pressure
Disadvantages - Dilutes colloid
osmotic pressure
- Promotes peripheral
oedem
- Higher incidence of
pulmpnary oedem
- Requires large
volume
- Effects are transient
-Expensive
-May produce coagulopathy (dextrans and
hetastarch)
-With capillary leaks may potentiate fluid loss to
the interstitium
-Impairs subsequent crossmatching of blood
(dextran)
-Dilutes clotting factors and platelet
-Decrease platelet adhesiveness (absorption onto
platelet membrane reseptor)
-Potential blocking of renal tubules and
reticuloendothelial cells in the liver
-Possible anaphylactoid reaction with dextran
CRYSTALLOID VS COLLOID
BLOOD TRANSFUSION:
GENERAL CONSIDERATION:
1 UNIT PACKED RED CELL INCREASE Hb
LEVEL UP TO 1 gr% AND HEMATOCRIT UP
TO 2 - 3% (ADULT)
TRANSFUSE PRC 10 ml/kgBW INCREASE Hb
LEVEL 3 gr%
MONITOR VITAL SIGNS AND DIURESIS
(1ml/kgBW/hr)
Kunci
Ingat urutan ABCD
Berikan oksigen pada semua kasus
trauma.
Beri infus cairan hangat (simpan cairan
di lemari tertutup dengan lampu 25
watt)
Darah, plasma, cairan yang
mengandung glukosa jangan dipanaskan
dalam microwave.
TERIMA KASIH
ATAS PERHATIANNYA
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- HEMATOKEZIADokumen58 halamanHEMATOKEZIAAnonymous 7xR3ymgBelum ada peringkat
- Morning Report AnestesiDokumen11 halamanMorning Report AnestesiHaryoko AnandaputraBelum ada peringkat
- PTT Tuberkulosis MiokarditisDokumen33 halamanPTT Tuberkulosis Miokarditisnina purnamasariBelum ada peringkat
- Diare Akut dengan Dehidrasi BeratDokumen24 halamanDiare Akut dengan Dehidrasi BeratMuhammad Fadhil RsBelum ada peringkat
- CRS HepatomaDokumen46 halamanCRS HepatomaalgutBelum ada peringkat
- Laporan Kasus HipertiroidDokumen50 halamanLaporan Kasus HipertiroidEkaBelum ada peringkat
- Tinpus Skin DeglovingDokumen14 halamanTinpus Skin DeglovingAhimsa MartawigunaBelum ada peringkat
- CRS Dermatitis Atopik AlhamdulillahDokumen23 halamanCRS Dermatitis Atopik Alhamdulillahalpha.orionBelum ada peringkat
- Terapi CairanDokumen60 halamanTerapi CairanRizna AriyaniBelum ada peringkat
- DIAGNOSA DINI UNTUK PENYAKIT JANTUNG KORONERDokumen25 halamanDIAGNOSA DINI UNTUK PENYAKIT JANTUNG KORONERHana YunikoBelum ada peringkat
- Morbus DuplayDokumen9 halamanMorbus DuplayHaziq AnuarBelum ada peringkat
- Amaurosis FugaxDokumen24 halamanAmaurosis FugaxlramalliBelum ada peringkat
- Terapi CairanDokumen4 halamanTerapi Cairanponco ajaBelum ada peringkat
- SkabiesDeteksiDokumen17 halamanSkabiesDeteksiHana YunikoBelum ada peringkat
- Laporan Kasus Hepatitis FulminanDokumen39 halamanLaporan Kasus Hepatitis FulminanmeldamirandaaBelum ada peringkat
- Laporan KasusDokumen44 halamanLaporan KasusBagoes Ario BimoBelum ada peringkat
- Terapi CairanDokumen31 halamanTerapi CairanInggriht Senny BondangBelum ada peringkat
- Referat Kelompok 33Dokumen11 halamanReferat Kelompok 33Sabella Gustika VernandaBelum ada peringkat
- JUDULDokumen21 halamanJUDULAdiBelum ada peringkat
- Referat Emfisema ParuDokumen20 halamanReferat Emfisema ParuTINA50% (2)
- Tata Laksana Atrial FibrilasiDokumen13 halamanTata Laksana Atrial Fibrilasifiras frsBelum ada peringkat
- Ppok Eksaserbasi AkutDokumen59 halamanPpok Eksaserbasi AkutPradnya Tika PutriBelum ada peringkat
- PRA PROPOSAL BAB 1-2 Widya Astriyani-Patklin-2006626424Dokumen13 halamanPRA PROPOSAL BAB 1-2 Widya Astriyani-Patklin-2006626424Widya AstriyaniBelum ada peringkat
- Gangguan HeparDokumen101 halamanGangguan HeparlukmanBelum ada peringkat
- Case UapDokumen25 halamanCase UapAudy AndanaBelum ada peringkat
- Tutorial Sken 3Dokumen22 halamanTutorial Sken 36130017019 MUHAMMAD RAIS FAISALBelum ada peringkat
- Kegawatdaruratan ParuDokumen104 halamanKegawatdaruratan ParuREFSIBelum ada peringkat
- Case Report Neonatus InfeksiDokumen37 halamanCase Report Neonatus InfeksiErwin ImawanBelum ada peringkat
- Lapsus GCM Jiwa GowaDokumen10 halamanLapsus GCM Jiwa GowaLuthfi Ziad AhmadBelum ada peringkat
- Kasus DHF Grade 2Dokumen9 halamanKasus DHF Grade 2Alif AdlanBelum ada peringkat
- ParotitisDokumen14 halamanParotitisShinta DewiBelum ada peringkat
- Ilmu Kedokteran ForensikDokumen36 halamanIlmu Kedokteran ForensikDiah Novianingsih Blue'zBelum ada peringkat
- Laporan Kasus SAHDokumen47 halamanLaporan Kasus SAHenggarwidyaBelum ada peringkat
- GAMBARAN RADIOLOGI PADA PPOKDokumen19 halamanGAMBARAN RADIOLOGI PADA PPOKrajaririnBelum ada peringkat
- Case ChikungunyaDokumen25 halamanCase ChikungunyaSilpi HamidiyahBelum ada peringkat
- Breast NeoplasmaDokumen13 halamanBreast NeoplasmaTira Wahyuni0% (1)
- Neurosis KardiakDokumen2 halamanNeurosis Kardiakadelina lubisBelum ada peringkat
- Tanda KematianDokumen14 halamanTanda KematianRegina Enggeline0% (1)
- DETEKSI DINI PENDENGARANDokumen43 halamanDETEKSI DINI PENDENGARANendy primaBelum ada peringkat
- Washed Red CellDokumen3 halamanWashed Red Cellera anggoro kusuma ningrum100% (1)
- Lapsus SepsisDokumen15 halamanLapsus SepsisJtanum100% (2)
- DETEKSI DINI GLAUKOMA NEOVASKULARDokumen4 halamanDETEKSI DINI GLAUKOMA NEOVASKULARRakhmat RamadhaniBelum ada peringkat
- Laporan Kasus Polisitemia Vera FixDokumen11 halamanLaporan Kasus Polisitemia Vera FixIqyu Chan KyuBelum ada peringkat
- CAP + Hemoptisis Ec Tumor Paru Kiri KelompokDokumen27 halamanCAP + Hemoptisis Ec Tumor Paru Kiri Kelompokfabiola wulurBelum ada peringkat
- KAD CovidDokumen24 halamanKAD CovidNita KurniasihBelum ada peringkat
- DEMAM TIFOIDDokumen19 halamanDEMAM TIFOIDYosiita KartinaaBelum ada peringkat
- Laporan Kasus Rehabilitasi Medik Stroke Non IskemikDokumen22 halamanLaporan Kasus Rehabilitasi Medik Stroke Non IskemikAnonymous hut4CmBelum ada peringkat
- EpididimitisDokumen48 halamanEpididimitissamsulBelum ada peringkat
- Penatalaksanaan Holistik FAMDokumen5 halamanPenatalaksanaan Holistik FAMnino123456Belum ada peringkat
- MumpsDokumen32 halamanMumpskeynechristaBelum ada peringkat
- GLAUKOMADokumen31 halamanGLAUKOMARaisa Desti ArdiantyBelum ada peringkat
- Laporan Kasus Anak Asma BronkhialDokumen39 halamanLaporan Kasus Anak Asma BronkhialSALMA HANINABelum ada peringkat
- Diagnosis PsikiatriDokumen21 halamanDiagnosis Psikiatriintan nur annisaBelum ada peringkat
- CAIRAN TERAPIDokumen27 halamanCAIRAN TERAPIMelody Nethania SutedjaBelum ada peringkat
- Mini Project PKMDokumen49 halamanMini Project PKMErma RoyaniBelum ada peringkat
- CASE Bedah Dwi OktaviliaDokumen40 halamanCASE Bedah Dwi OktaviliaPurryBelum ada peringkat
- TERAPI SYOKDokumen36 halamanTERAPI SYOKBetrice KotanBelum ada peringkat
- Terapi Cairan Pada Syok HipovolemikDokumen36 halamanTerapi Cairan Pada Syok Hipovolemikcr4zykunBelum ada peringkat
- CirculationDokumen26 halamanCirculationSunu MurtiBelum ada peringkat
- Materi SyokDokumen65 halamanMateri SyokNesha MaharnBelum ada peringkat
- Standar Praktik Profesi KeperawatanDokumen27 halamanStandar Praktik Profesi KeperawatananchemeysBelum ada peringkat
- Peran Perawat JiwaDokumen10 halamanPeran Perawat JiwaanchemeysBelum ada peringkat
- Aspek Etik Dan Legal Dalam Keperawatan IntensifDokumen13 halamanAspek Etik Dan Legal Dalam Keperawatan IntensifanchemeysBelum ada peringkat
- Konsep diri anak jalanan remajaDokumen20 halamanKonsep diri anak jalanan remajaanchemeysBelum ada peringkat
- Materi Berpikir Kritis 11 Maret 2022Dokumen25 halamanMateri Berpikir Kritis 11 Maret 2022anchemeysBelum ada peringkat
- Penatalaksanaan Kegawatdaruratan Sistem PernafasanDokumen12 halamanPenatalaksanaan Kegawatdaruratan Sistem PernafasananchemeysBelum ada peringkat
- Mental History - AnceDokumen14 halamanMental History - AnceanchemeysBelum ada peringkat
- Resume Kasus b2Dokumen16 halamanResume Kasus b2anchemeysBelum ada peringkat
- Presentation 1Dokumen34 halamanPresentation 1anchemeysBelum ada peringkat
- SAP Sirosis HepatisDokumen5 halamanSAP Sirosis HepatisanchemeysBelum ada peringkat
- Presentation 3Dokumen13 halamanPresentation 3anchemeysBelum ada peringkat
- Leaflet SHDokumen2 halamanLeaflet SHanchemeysBelum ada peringkat
- Pembekalan Penelitian KualitatifDokumen10 halamanPembekalan Penelitian KualitatifanchemeysBelum ada peringkat
- Model Konsep Keperawatan KeluargaDokumen24 halamanModel Konsep Keperawatan KeluargaanchemeysBelum ada peringkat
- Tatalaksana Anafilaksis Secara UmumDokumen3 halamanTatalaksana Anafilaksis Secara UmumanchemeysBelum ada peringkat
- Sap RomDokumen31 halamanSap RomanchemeysBelum ada peringkat
- PrintDokumen29 halamanPrintanchemeysBelum ada peringkat
- TRANSPORAKTIFDokumen10 halamanTRANSPORAKTIFanchemeysBelum ada peringkat
- Asuhan Keperawatan Pada Pasien Transplantasi GinjalDokumen8 halamanAsuhan Keperawatan Pada Pasien Transplantasi GinjalHimawarie CheppyBelum ada peringkat
- SAP KemoDokumen33 halamanSAP KemoanchemeysBelum ada peringkat
- Leaflet B6Dokumen3 halamanLeaflet B6anchemeysBelum ada peringkat
- Leaflet B6Dokumen3 halamanLeaflet B6anchemeysBelum ada peringkat
- Fenomenologi Metode KualitatifDokumen19 halamanFenomenologi Metode KualitatifanchemeysBelum ada peringkat
- MODUL Pencernaan IIDokumen19 halamanMODUL Pencernaan IIanchemeysBelum ada peringkat
- Cara Meningkatkan Caring Pada Perawat Melalui PendidikanDokumen18 halamanCara Meningkatkan Caring Pada Perawat Melalui PendidikananchemeysBelum ada peringkat
- Pendekatan Perilaku KepemimpinanDokumen11 halamanPendekatan Perilaku Kepemimpinananchemeys100% (1)
- Asuhan Keperawatan Pada Pasien Transplantasi GinjalDokumen8 halamanAsuhan Keperawatan Pada Pasien Transplantasi GinjalHimawarie CheppyBelum ada peringkat
- Komunikasi Efektif - 2015Dokumen42 halamanKomunikasi Efektif - 2015anchemeysBelum ada peringkat
- Bermain Dan HospitalisasiDokumen30 halamanBermain Dan HospitalisasianchemeysBelum ada peringkat
- Komunikasi Efektif - 2015Dokumen42 halamanKomunikasi Efektif - 2015anchemeysBelum ada peringkat