0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
158 tayangan23 halamanStruktur dan Komposisi Enamel Gigi
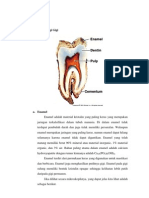
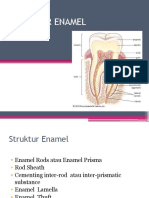
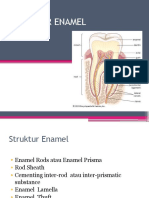
Enamel merupakan jaringan keras yang terbentuk di permukaan gigi. Terdiri atas 96% kristal hidroksiapatit yang memberikan sifat keras. Terbentuk dari ameloblast selama proses amelogenesis yang terbagi menjadi tahap prasekresi, sekresi, dan maturasi. Memiliki struktur prisma yang mengandung kristal berukuran besar untuk mendukung fungsi kunyahan. Permukaan email lebih tebal dan keras dibanding bagian dalam untuk melindungi
Diunggah oleh
isabellahHak Cipta
© © All Rights Reserved
Kami menangani hak cipta konten dengan serius. Jika Anda merasa konten ini milik Anda, ajukan klaim di sini.
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PPTX, PDF, TXT atau baca online di Scribd
0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
158 tayangan23 halamanStruktur dan Komposisi Enamel Gigi
Enamel merupakan jaringan keras yang terbentuk di permukaan gigi. Terdiri atas 96% kristal hidroksiapatit yang memberikan sifat keras. Terbentuk dari ameloblast selama proses amelogenesis yang terbagi menjadi tahap prasekresi, sekresi, dan maturasi. Memiliki struktur prisma yang mengandung kristal berukuran besar untuk mendukung fungsi kunyahan. Permukaan email lebih tebal dan keras dibanding bagian dalam untuk melindungi
Diunggah oleh
isabellahHak Cipta
© © All Rights Reserved
Kami menangani hak cipta konten dengan serius. Jika Anda merasa konten ini milik Anda, ajukan klaim di sini.
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PPTX, PDF, TXT atau baca online di Scribd